JavaScript Basic Notes
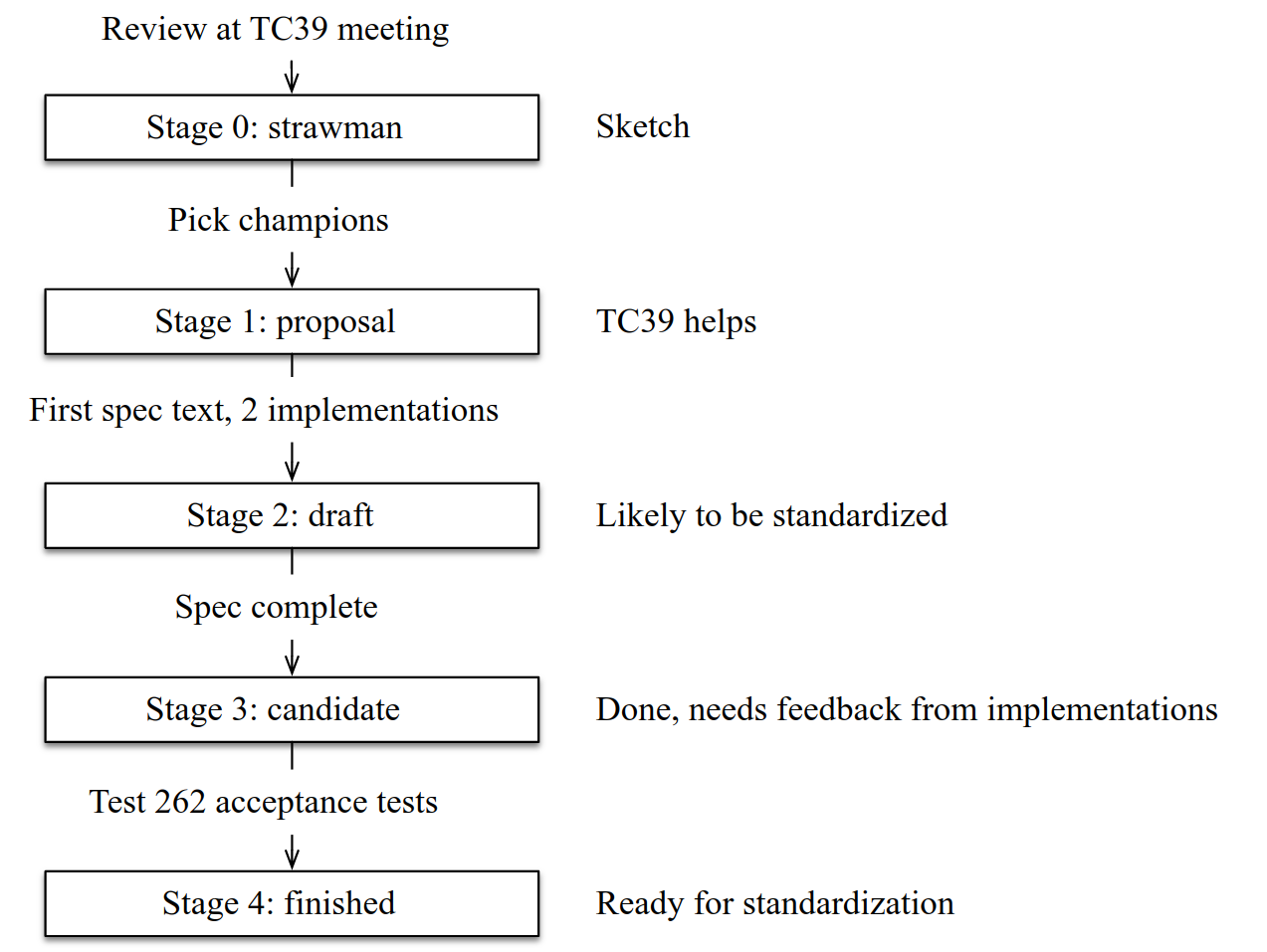
TC39
JavaScript = ECMAScript + DOM + BOM:
- ECMAScript: ECMA-262.
- DOM: DOM Core + DOM HTML (
document). - BOM: Browser Object Model API (HTML5)
(
window/navigator/location/screen/performanceetc).
Primitive Values
Primitive data types:
- Undefined.
- Null.
- Boolean.
- Number.
- String.
- Symbol.
- BigInt.
Undefined
- 对象属性未定义时, 该属性值为
undefined. - 未初始化变量的初值为
undefined(表示等待被赋值).
Null
当引用为空或引用对象不存在时, 值为 null.
null 值表示一个空对象指针.
typeof null -> object.
Boolean
Zero Value Expression
零值表达式:
undefined.null.false.NaN.00n.''.
Boolean Conversion
x | Boolean(x) |
|---|---|
undefined | false |
null | false |
boolean | x |
number | 0 → false, NaN → false |
Other numbers → true | |
bigint | 0n → false |
Other numbers → true | |
string | '' → false |
Other strings → true | |
symbol | true |
object | true |
Number
- Binary:
0b10/0B10. - Octal:
0o23/0O23. - Hex:
0xFF. **指数运算符.- BigInt.
const a = 2172141653
const b = 15346349309
const c1 = a * b
// => 33334444555566670000
const c2 = BigInt(a) * BigInt(b)
// => 33334444555566667777n
const inhabitantsOfLondon = 1_335_000
const distanceEarthSunInKm = 149_600_000
const fileSystemPermission = 0b111_111_000
const bytes = 0b1111_10101011_11110000_00001101
const words = 0xF3B_F00D
const massOfElectronInKg = 9.109_383_56e-31
const trillionInShortScale = 1e1_2
Number Conversion
x | Number(x) |
|---|---|
undefined | NaN |
null | 0 |
boolean | false → 0, true → 1 |
number | x |
bigint | -1n → -1, 1n → 1 |
string | '' → 0 |
| Other → parsed number, ignoring leading/trailing whitespace | |
symbol | Throws TypeError |
object | Configurable ([Symbol.toPrimitive]()/valueOf()) |
assert.equal(Number(123.45), 123.45)
assert.equal(Number(''), 0)
assert.equal(Number('\n 123.45 \t'), 123.45)
assert.equal(Number('xyz'), Number.NaN)
assert.equal(Number(-123n), -123)
assert.equal(
Number({
valueOf() {
return 123
},
}),
123
)
Number Static Properties
Number.NaN.Number.NEGATIVE_INFINITY.Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY.Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER.Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER.Number.EPSILON.Number.isNaN().Number.isFinite().Number.isInteger().Number.isSafeInteger().Number.toExponential().Number.toFixed().Number.toPrecision().Number.parseInt(string, radix).Number.parseFloat(string).
;(1234).toExponential()
// '1.234e+3'
;(1234).toExponential(5)
// '1.23400e+3'
;(1234).toExponential(1)
// '1.2e+3'
;(0.003).toExponential()
// '3e-3'
;(0.00000012).toFixed(10)
// '0.0000001200'
;(0.00000012).toFixed()
// '0'
;(10 ** 21).toFixed()
// '1e+21'
;(1234).toPrecision(3)
// '1.23e+3'
;(1234).toPrecision(4)
// '1234'
;(1234).toPrecision(5)
// '1234.0'
;(1.234).toPrecision(3)
// '1.23'
Not A Number
const numberType = typeof Number.NaN // 'number'
Number.isFinite(Number.NaN)
// false
Number.isNaN(Number.NaN)
// true
Number.isNaN(123)
// false
Number.isNaN('abc')
// false
function isNumber(value) {
return typeof value === 'number' && Number.isFinite(value)
}
NaN === NaN -> false.
Infinity Number
Infinity represents all values greater than 1.7976931348623157e+308.
Infinity will be converted to null with JSON.stringify().
const largeNumber = 1.7976931348623157e308
// eslint-disable-next-line no-loss-of-precision -- Infinity
const largerNumber = 1.7976931348623157e309
console.log(largeNumber) // 1.7976931348623157e+308
console.log(largerNumber) // Infinity
console.log(46 / 0) // Infinity
console.log(Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY) // Infinity
console.log(Number.MAX_VALUE) // Infinity
// eslint-disable-next-line no-loss-of-precision -- -Infinity
console.log(-1.7976931348623157e309) // -Infinity
console.log(-46 / 0) // -Infinity
console.log(Number.NEGATIVE_INFINITY) // -Infinity
console.log(Number.MIN_VALUE) // -Infinity
console.log(Math.max()) // -Infinity
console.log(Math.min()) // Infinity
Number.isFinite(Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY)
// false
Number.isFinite(Number.NEGATIVE_INFINITY)
// false
Number.isFinite(Number.NaN)
// false
Number.isFinite(123)
// true
Safe Number
- Safe integers:
- Precision: 53 bits plus sign.
- Range: (
−2^53,2^53).
- Array indices:
- Precision: 32 bits, unsigned
- Range: [
0,2^32−1). - Typed Arrays have a larger range of 53 bits (safe and unsigned).
- Bitwise operators:
- Precision: 32 bits.
- Range of unsigned right shift (
>>>): unsigned, [0,2^32). - Range of all other bitwise operators: signed, [
−2^31,2^31).
assert.equal(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER, 2 ** 53 - 1)
assert.equal(Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER, -Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER)
assert.equal(Number.isSafeInteger(5), true)
assert.equal(Number.isSafeInteger('5'), false)
assert.equal(Number.isSafeInteger(5.1), false)
assert.equal(Number.isSafeInteger(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER), true)
assert.equal(Number.isSafeInteger(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER + 1), false)
Number.isInteger(-17)
// true
Number.isInteger(33)
// true
Number.isInteger(33.1)
// false
Number.isInteger('33')
// false
Number.isInteger(Number.NaN)
// false
Number.isInteger(Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY)
// false
Float Number
- 计算浮点数时, 应先计算整数, 再利用移位/乘法/除法转化为浮点数.
- 浮点值的精确度最高可达 17 位小数.
const a = (1 + 2) / 10 // a = 0.1 + 0.2;
String
String Primitive Features
作为基本变量:
delete无法删除某位字符.
String Reference Features
- 赋值与传参: 传递 string 字符串常量的引用.
- 所有 string 字面量都是不可变量, 当对 string 进行操作后, 将先会在堆区创建副本, 再通过副本进行修改, 并返回副本的索引.
for...in: 返回下标数字.for...of: 对字符串字符进行遍历.- 没有被任何变量引用的 string: 垃圾回收.
const goodString = 'I\'ve been a good string'
console.log(typeof goodString) // string
console.log(goodString instanceof String) // false
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(goodString)) // [object String]
// eslint-disable-next-line no-new-wrappers, unicorn/new-for-builtins
const badString = new String('I\'ve been a naughty string')
console.log(typeof badString) // object
console.log(badString instanceof String) // true
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(badString)) // [object String]
const isPrimitiveString = value => typeof value === 'string'
console.log(isPrimitiveString(goodString)) // true
console.log(isPrimitiveString(badString)) // false
const isObjectWrappedString = value => value instanceof String
console.log(isObjectWrappedString(goodString)) // false
console.log(isObjectWrappedString(badString)) // true
const isString = value => typeof value === 'string' || value instanceof String
console.log(isString(goodString)) // true
console.log(isString(badString)) // true
function isStringAlternative(value) {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(badString) === '[object String]'
}
console.log(isStringAlternative(goodString)) // true
console.log(isStringAlternative(badString)) // true
String Conversion
x | String(x) |
|---|---|
undefined | 'undefined' |
null | 'null' |
boolean | false → 'false', true → 'true' |
number | 123 → '123' |
bigint | 123n → '123' |
string | x |
symbol | Symbol('abc') → 'Symbol(abc)' |
object | Configurable (toPrimitive/toStringTag/toString()) |
String Unicode
// eslint-disable-next-line no-self-compare
const truthy = 'z' === 'z' // true
const truthy = '\x7A' === 'z' // true
const truthy = '\u007A' === 'z' // true
const truthy = '\u{7A}' === 'z' // true
String Char Code
string.charAt(index).string.charCodeAt(index).string.fromCharCode(charCode).string.codePointAt(index): 正确处理 4 字节存储字符.string.fromCodePoint(codePoint): 正确处理 4 字节存储字符.
function is32Bit(c) {
return c.codePointAt(0) > 0xFFFF
}
const truthy = String.fromCodePoint(0x78, 0x1F680, 0x79) === 'x\uD83D\uDE80y'
const after = before.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + before.slice(1)
String Slice and Merge
string.slice().string.substring().string.substr().string.split(separator): 选择割断符, 返回字符串数组.Array<string>.join(separator): 将字符串数组连接成字符串.
const stringValue = 'hello world'
console.log(stringValue.slice(3)) // "lo world"
console.log(stringValue.substring(3)) // "lo world"
console.log(stringValue.substr(3)) // "lo world"
console.log(stringValue.slice(3, 8)) // "lo wo"
console.log(stringValue.substring(3, 8)) // "lo wo"
console.log(stringValue.substr(3, 8)) // "lo world"
console.log(stringValue.slice(-3)) // "rld"
console.log(stringValue.substring(-3)) // "hello world"
console.log(stringValue.substr(-3)) // "rld"
console.log(stringValue.slice(3, -4)) // "lo w"
console.log(stringValue.substring(3, -4)) // "hel"
console.log(stringValue.substr(3, -4)) // "" (empty string)
String Query
string.includes(substr).string.startsWith(substr).string.endsWith(substr).- 使用第二个参数 n 时, endsWith 针对前 n 个字符, 其他两个方法针对从第 n 个位置直到字符串结束.
const s = 'Hello world!'
s.startsWith('world', 6) // true
s.endsWith('Hello', 5) // true
s.includes('Hello', 6) // false
// Arrays difference
;[
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[5, 2, 10],
].reduce((a, b) => a.filter(c => !b.includes(c)))
// [1, 3, 4]
// Arrays intersection
;[
[1, 2, 3],
[101, 2, 1, 10],
[2, 1],
].reduce((a, b) => a.filter(c => b.includes(c)))
// [1, 2]
string.match(RegExp): string[] | null.string.matchAll(RegExp): string[] | null.
interface RegExpMatchArray extends Array<string> {
index: number
input: string
groups: Record<string, string> | undefined
}
string.search(string | RegExp): number.
'a2b'.search(/\d/)
// 1
'a2b'.search('[0-9]')
// 1
String Replace
string.replace(string | RegExp, replaceValue | replacerFunction).string.replaceAll(string | RegExp, replaceValue | replacerFunction).
// eslint-disable-next-line prefer-regex-literals
const regexp = new RegExp('foo[a-z]*', 'g')
const str = 'table football, foosball'
const matches = str.matchAll(regexp)
for (const match of matches) {
console.log(
`Found ${match[0]} start=${match.index} end=${
match.index + match[0].length
}.`
)
}
// expected output: "Found football start=6 end=14."
// expected output: "Found foosball start=16 end=24."
// matches iterator is exhausted after the for..of iteration
// Call matchAll again to create a new iterator
Array.from(str.matchAll(regexp), m => m[0])
// Array [ "football", "foosball" ]
'aabbcc'.replaceAll('b', '.')
// => 'aa..cc'
'aabbcc'.replaceAll(/b/g, '.')
// => 'aa..cc'
String Pad
string.repeat(times).
'hello'.repeat(2) // "hellohello"
'na'.repeat(2.9) // "nana"
'na'.repeat(-0.9) // ""
'na'.repeat(-1) // RangeError
'na'.repeat(Number.NaN) // ""
'na'.repeat(Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY) // RangeError
'na'.repeat('na') // ""
'na'.repeat('3') // "nanana"
string.padStart(len, paddingStr).string.padEnd(len, paddingStr).
'1'.padStart(10, '0') // "0000000001"
'12'.padStart(10, '0') // "0000000012"
'123456'.padStart(10, '0') // "0000123456"
'12'.padStart(10, 'YYYY-MM-DD') // "YYYY-MM-12"
'09-12'.padStart(10, 'YYYY-MM-DD') // "YYYY-09-12"
String Trim
string.trimLeft()/string.trimStart(): remove start whitespace.string.trimRight()/string.trimEnd(): remove end whitespace.
String Template Literals
str 表示模板字符串:
// 普通字符串
;`In JavaScript '\n' is a line-feed.``\`Yo\` World!``In JavaScript this is // 多行字符串
not legal.``${
x // 引用变量
} + ${y * 2} = ${x + y * 2}``${obj.x + obj.y}``foo ${
fn() // 调用函数
} bar`
Tagged Templates Literals
function boldify(parts, ...insertedParts) {
return parts
.map((s, i) => {
if (i === insertedParts.length)
return s
return `${s}<strong>${insertedParts[i]}</strong>`
})
.join('')
}
const name = 'Sabertaz'
console.log(boldify`Hi, my name is ${name}!`)
// => "Hi, my name is <strong>Sabertaz</strong>!"
function template(strings, ...keys) {
return function (...values) {
const dict = values[values.length - 1] || {}
const result = [strings[0]]
keys.forEach((key, i) => {
const value = Number.isInteger(key) ? values[key] : dict[key]
result.push(value, strings[i + 1])
})
return result.join('')
}
}
const t1Closure = template`${0}${1}${0}!`
t1Closure('Y', 'A') // "YAY!"
const t2Closure = template`${0} ${'foo'}!`
t2Closure('Hello', { foo: 'World' }) // "Hello World!"
编译模板 (小型模板引擎):
function compile(template) {
const evalExpr = /<%=(.+?)%>/g
const expr = /<%([\s\S]+?)%>/g
template = template
.replace(evalExpr, '`); \n echo( $1 ); \n echo(`')
.replace(expr, '`); \n $1 \n echo(`')
template = `echo(\`${template}\`);`
const script = `(function parse(data){
let output = "";
function echo(html){
output += html;
}
${template}
return output;
})`
return script
}
const template = `
<ul>
<% for(let i=0; i < data.supplies.length; i++) { %>
<li><%= data.supplies[i] %></li>
<% } %>
</ul>
`
const parse = compile(template)
div.innerHTML = parse({ supplies: ['broom', 'mop', 'cleaner'] })
// => <ul>
// => <li>broom</li>
// => <li>mop</li>
// => <li>cleaner</li>
// => </ul>
// 下面的hashTemplate函数
// 是一个自定义的模板处理函数
const libraryHtml = hashTemplate`
<ul>
#for book in ${myBooks}
<li><i>#{book.title}</i> by #{book.author}</li>
#end
</ul>
`
国际化处理:
i18n`Welcome to ${siteName}, you are visitor number ${visitorNumber}!`
// "欢迎访问xxx, 您是第xxxx位访问者!"
XSS protection:
const message = SaferHTML`<p>${sender} has sent you a message.</p>`
function SaferHTML(templateString, ...expressions) {
let s = templateString[0]
for (let i = 0; i < expressions.length; i++) {
const expression = String(expressions[i])
// Escape special characters in the substitution.
s += expression
.replace(/&/g, '&')
.replace(/</g, '<')
.replace(/>/g, '>')
// Don't escape special characters in the template.
s += templateString[i + 1]
}
return s
}
运行代码:
jsx`
<div>
<input
ref='input'
onChange='${this.handleChange}'
defaultValue='${this.state.value}' />
${this.state.value}
</div>
`
java`
class HelloWorldApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!"); // Display the string.
}
}
`
HelloWorldApp.main()
Raw String
console.log(`\u00A9`) // ©
console.log(String.raw`\u00A9`) // \u00A9
console.log(`first line\nsecond line`)
// first line
// second line
console.log(String.raw`first line\nsecond line`)
// "first line\nsecond line"
function printRaw(strings) {
console.log('Actual characters:')
for (const string of strings)
console.log(string)
console.log('Escaped characters;')
for (const rawString of strings.raw)
console.log(rawString)
}
printRaw`\u00A9${'and'}\n`
// Actual characters:
// ©
// (换行符)
// Escaped characters:
// \u00A9
// \n
String Utils
function ucWords(string) {
return string.toLowerCase().replace(/\b[a-z]/g, l => l.toUpperCase())
}
function ucFirst(string) {
return string[0].toUpperCase() + string.substr(1)
}
function studlyCase(string) {
return string
.replace('-', ' ')
.replace('_', ' ')
.split(' ')
.map(str => str[0].toUpperCase() + str.substr(1).toLowerCase())
.join('')
}
function snakeCase(string, glue = '_') {
return string
.replace(/\W+/g, ' ')
.split(/ |\B(?=[A-Z])/)
.map(word => word.toLowerCase())
.join(glue)
}
function kebabCase(string) {
return snakeCase(string, '-')
}
function objectToQueryString(obj) {
return Object.keys(obj)
.reduce((carry, key) => {
if (obj[key] || obj[key] === 0)
return `${carry}${key}=${obj[key]}&`
return carry
}, '')
.replace(/&+$/, '')
}
Symbol
- A Symbol is a unique and immutable primitive value and may be used as the key of an Object property.
- Symbols don't auto-convert to strings and can't convert to numbers.
Symbol.for(key)create global Symbol registry.
// eslint-disable-next-line symbol-description
const genericSymbol = Symbol()
// eslint-disable-next-line symbol-description
const otherGenericSymbol = Symbol()
console.log(genericSymbol === otherGenericSymbol) // false
const fooSymbol = Symbol('foo')
const otherFooSymbol = Symbol('foo')
console.log(fooSymbol === otherFooSymbol) // false
const fooGlobalSymbol = Symbol.for('foobar') // 创建新符号
const otherFooGlobalSymbol = Symbol.for('foobar') // 重用已有符号
console.log(fooGlobalSymbol === otherFooGlobalSymbol) // true
Symbol Conversion
| Convert To | Explicit Conversion | Coercion (Implicit Conversion) |
|---|---|---|
boolean | Boolean(sym) → OK | !sym → OK |
number | Number(sym) → TypeError | sym * 2 → TypeError |
string | String(sym) → OK | '' + sym → TypeError |
sym.toString() → OK | ${sym} → TypeError | |
object | Object(sym) → OK | Object.keys(sym) → OK |
Built-in Symbol Methods
[Symbol.iterator]():for of.[Symbol.asyncIterator]():for await of.[Symbol.match/replace/search/split](target):string.match/replace/search/split(classWithSymbolFunction).[Symbol.hasInstance](instance):instance of.[Symbol.species](): constructor for making derived objects.[Symbol.toPrimitive](hint): 强制类型转换.[Symbol.toStringTag](): string used byObject.prototype.toString().
iterator:
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c']
const iter = arr[Symbol.iterator]()
iter.next() // { value: 'a', done: false }
iter.next() // { value: 'b', done: false }
iter.next() // { value: 'c', done: false }
iter.next() // { value: undefined, done: true }
hasInstance:
class Bar {}
class Baz extends Bar {
static [Symbol.hasInstance](instance) {
return false
}
}
const b = new Baz()
console.log(Bar[Symbol.hasInstance](b)) // true
console.log(b instanceof Bar) // true
console.log(Baz[Symbol.hasInstance](b)) // false
console.log(b instanceof Baz) // false
const ReferenceType = {
[Symbol.hasInstance](value) {
return (
value !== null
&& (typeof value === 'object' || typeof value === 'function')
)
},
}
const obj1 = {}
console.log(obj1 instanceof Object) // true
console.log(obj1 instanceof ReferenceType) // true
const obj2 = Object.create(null)
console.log(obj2 instanceof Object) // false
console.log(obj2 instanceof ReferenceType) // true
species:
class MyClass {
static get [Symbol.species]() {
return this
}
constructor(value) {
this.value = value
}
clone() {
return new this.constructor[Symbol.species](this.value)
}
}
class MyDerivedClass1 extends MyClass {
// empty
}
class MyDerivedClass2 extends MyClass {
static get [Symbol.species]() {
return MyClass
}
}
const instance1 = new MyDerivedClass1('foo')
const instance2 = new MyDerivedClass2('bar')
const clone1 = instance1.clone()
const clone2 = instance2.clone()
console.log(clone1 instanceof MyClass) // true
console.log(clone1 instanceof MyDerivedClass1) // true
console.log(clone2 instanceof MyClass) // true
console.log(clone2 instanceof MyDerivedClass2) // false
toPrimitive:
class Temperature {
constructor(degrees) {
this.degrees = degrees
}
[Symbol.toPrimitive](hint) {
switch (hint) {
case 'string':
return `${this.degrees}\u00B0` // degrees symbol
case 'number':
return this.degrees
case 'default':
return `${this.degrees} degrees`
}
}
}
const freezing = new Temperature(32)
console.log(`${freezing}!`) // "32 degrees!"
console.log(freezing / 2) // 16
console.log(String(freezing)) // "32째"
toStringTag:
class Person {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name
}
get [Symbol.toStringTag]() {
return 'Person'
}
}
const me = new Person('Me')
console.log(me.toString()) // "[object Person]"
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(me)) // "[object Person]"
| Value | toString Tag |
|---|---|
| undefined | Undefined |
| null | Null |
| Array object | Array |
| string object | String |
| arguments | Arguments |
| callable | Function |
| error object | Error |
| boolean object | Boolean |
| number object | Number |
| date object | Date |
| regular expression object | RegExp |
| (Otherwise) | Object |
Bigint
- Decimal:
123n. - Binary:
0b1101n. - Octal:
0o777n. - Hexadecimal:
0xFFn.
/**
* Takes a bigint as an argument and returns a bigint
*/
function nthPrime(nth) {
if (typeof nth !== 'bigint')
throw new TypeError('Not bigint')
function isPrime(p) {
for (let i = 2n; i < p; i++) {
if (p % i === 0n)
return false
}
return true
}
for (let i = 2n; ; i++) {
if (isPrime(i)) {
if (--nth === 0n)
return i
}
}
}
assert.deepEqual(
[1n, 2n, 3n, 4n, 5n].map(nth => nthPrime(nth)),
[2n, 3n, 5n, 7n, 11n]
)
Bigint Conversion
x | BigInt(x) |
|---|---|
undefined | Throws TypeError |
null | Throws TypeError |
boolean | false → 0n, true → 1n |
number | 123 → 123n |
| Non-integer → throws RangeError | |
bigint | x |
string | '123' → 123n |
| Unparsable → throws SyntaxError | |
symbol | Throws TypeError |
object | Configurable ([Symbol.toPrimitive]()/valueOf()) |
BigInt(undefined)
// TypeError: Cannot convert undefined to a BigInt
BigInt(null)
// TypeError: Cannot convert null to a BigInt
BigInt('abc')
// SyntaxError: Cannot convert abc to a BigInt
BigInt('123n')
// SyntaxError: Cannot convert 123n to a BigInt
BigInt('123')
// 123n
BigInt('0xFF')
// 255n
BigInt('0b1101')
// 13n
BigInt('0o777')
// 511n
BigInt(123.45)
// RangeError: The number 123.45 cannot be converted to a BigInt
BigInt(123)
// 123n
BigInt({
valueOf() {
return 123n
},
})
// 123n
| Convert To | Explicit Conversion | Coercion (Implicit Conversion) |
|---|---|---|
boolean | Boolean(0n) → false | !0n → true |
Boolean(int) → true | !int → false | |
number | Number(7n) → 7 | +int → TypeError |
string | String(7n) → '7' | ''+7n → '7' |
Bigint Static Properties
BigInt.asIntN(width, theInt): Casts theInt to width bits (signed).BigInt.asUintN(width, theInt): Casts theInt to width bits (unsigned).
const uint64a = BigInt.asUintN(64, 12345n)
const uint64b = BigInt.asUintN(64, 67890n)
const result = BigInt.asUintN(64, uint64a * uint64b)
Wrapper Objects for Primitives
Using the wrapper function without the new keyword is a useful way of coercing a value into a primitive type.
// Not recommended (primitive object wrapper):
// eslint-disable-next-line no-new-wrappers, unicorn/new-for-builtins
const objectType = typeof new String(37) // object
// Safe (type coercion with wrapper function):
const stringType = typeof String(37) // string
// Primitive strings:
// eslint-disable-next-line no-self-compare
const truthy = '37' === '37' // true
// Object-wrapped string:
// eslint-disable-next-line no-new-wrappers, unicorn/new-for-builtins
const falsy = new String(37) === '37' // false
// Type-coerced string:
const truthy = String(37) === '37' // true
// BAD!
// eslint-disable-next-line no-new-wrappers, unicorn/new-for-builtins
const falseObject = new Boolean(false)
const result = falseObject && true
console.log(result) // true
console.log(typeof falseObject) // object
console.log(falseObject instanceof Boolean) // true
const prim = true
assert.equal(typeof prim, 'boolean')
assert.equal(prim instanceof Boolean, false)
// eslint-disable-next-line unicorn/new-for-builtins
const wrapped = Object(prim)
assert.equal(typeof wrapped, 'object')
assert.equal(wrapped instanceof Boolean, true)
assert.equal(wrapped.valueOf(), prim) // unwrap
Box and Unbox for primitive values:
- 自动创建的原始值包装对象可以让原始值拥有对象的行为.
- 自动创建的原始值包装对象只存在于访问它的那行代码执行期间.
- 常数值加括号可转化为对象.
- 可以对 primitive values 进行 ES6 解构语法.
const s1 = 'some text'
const s2 = s1.substring(2) // Call method on primitive string.
// let _s1 = new String(s1);
// const s2 = _s1.substring(2);
// _s1 = null;
const s3 = 'some text'
s3.color = 'red'
console.log(s3.color) // undefined
// primitive string
const greet = 'Hello there'
// primitive is converted to an object
// in order to use the split() method
const hello = greet.split(' ')[0] // "Hello"
// attempting to augment a primitive is not an error
greet.smile = true
// but it doesn't actually work
const undef = typeof greet.smile // "undefined"
不使用 new 关键字,包装类构造函数返回值为基本类型
const numberType = typeof Number(1) // "number"
const numberType = typeof Number('1') // "number"
// eslint-disable-next-line no-new-wrappers, unicorn/new-for-builtins
const numberType = typeof Number(new Number()) // "number"
const stringType = typeof String(1) // "string"
const booleanType = typeof Boolean(1) // "boolean"
Reference Values
- Object e.g Date, RegExp.
- Function.
- Array.
- Map.
- Set.
- WeakMap.
- WeakSet.
Array
- 与 Object 同源.
- 关联数组:
arrayName["string"] = value;实际为 Array 对象添加属性{string:value}. - 缓存数组长度:
int l = list.length(访问length造成运算). []数组,{}对象.- 数组在数值运算环境中转化为 0 (空数组)/ num (单一元素数组)/NaN (多元素数组/NaN 数组).
const array = [...Array.from({ length: 5 }).keys()] // => [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
Array Length
- 数组下标满足 [0, 2^32-1) 即可
- 运用大于 length 的下标, length 自动增大, 不会发生数组边界错误
- length 等于 数组最后一个整数属性名+1, length 不一定等于 数组中有效元素个数
Array Literals
不使用构造函数,使用数组字面量创建数组
const arr1 = Array.from({ length: 3 }) // 数组长度
const arr2 = Array.from({ length: 3.14 }) // RangeError
if (typeof Array.isArray === 'undefined') {
Array.isArray = function (arg) {
// 其余对象返回值 [object Object/Number/String/Boolean]
return Object.prototype.toString.call(arg) === '[object Array]'
}
}
Array Of
Array.of(1) // [1]
Array.of(1, 2, 3) // [1, 2, 3]
Array.of(undefined) // [undefined]
Array From
强大的函数式方法:
- 伪数组对象 (Array-like object).
- 可枚举对象 (Iterable object).
- 浅克隆数组 (Shallow Clone).
map函数.
interface ArrayLike<T> {
length: number
[n: number]: T
}
interface Array {
from: (<T>(iterable: Iterable<T> | ArrayLike<T>) => T[]) & (<T, U>(
iterable: Iterable<T> | ArrayLike<T>,
mapFunc: (v: T, i: number) => U,
thisArg?: any
) => U[])
}
// Set
// Map
// NodeList 对象
const ps = document.querySelectorAll('p')
Array.from(ps).forEach((p) => {
console.log(p)
})
// arguments 对象
function foo() {
// eslint-disable-next-line prefer-rest-params
const args = Array.from(arguments)
// ...
}
Array.from('hello')
// => ['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o']
const namesSet = new Set(['a', 'b'])
Array.from(namesSet) // ['a', 'b']
// 克隆数组
Array.from([1, 2, 3])
// => [1, 2, 3]
Array.from(arrayLike, x => x * x)
// =>
Array.from(arrayLike).map(x => x * x)
Array.from([1, 2, 3], x => x * x)
// [1, 4, 9]
// random array generation
Array.from(Array.from({ length: 5 }).keys())
// [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
// Typed array initialization
Array.from<T>({ length: maxSize }).fill(initValue)
Array Fill
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4]
numbers.fill(1, 2)
console.log(numbers.toString()) // 1, 2, 1, 1
numbers.fill(0, 1, 3)
console.log(numbers.toString()) // 1, 0, 0, 1
numbers.fill(1)
console.log(numbers.toString()) // 1, 1, 1, 1
Array CopyWithin
copyWithin(dest, start, end), 替换数组元素, 修改原数组:
;[1, 2, 3, 4, 5].copyWithin(0, 3)
// => [4, 5, 3, 4, 5]
;[1, 2, 3, 4, 5].copyWithin(0, -2, -1)
// -2相当于3号位, -1相当于4号位
// => [4, 2, 3, 4, 5]
// 将2号位到数组结束, 复制到0号位
const i32a = new Int32Array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
i32a.copyWithin(0, 2)
// => Int32Array [3, 4, 5, 4, 5]
Array Stack
arr.unshift(value) // 添加数组首元素
arr.push(value) // 添加数组尾元素
arr.shift() // 删除数组首元素
arr.pop() // 删除数组尾元素
Array Slice and Merge
- slice 不改变原数组, splice 改变原数组.
;[].slice(start, end) // [start] - [end - 1]
;[].splice(startIndex, lengthToDelete, insertElements) // 功能强大的多态方法
;[].concat(otherArray)
;[].join(separator)
Array Query
;[].at(index) // ES2022
;[].includes(element) // boolean.
;[].find(callback) // element.
;[].findIndex(callback) // element index.
;[].indexOf(element) // -1 or other.
;[].lastIndexOf(element) // -1 or other.
// console.log([NaN].indexOf(NaN));
// -1
console.log([Number.NaN].includes(Number.NaN))
// true
Array Element Filter
相当于 Haskell 中的 List Filter:
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
const filterResult = numbers.filter((item, index, array) => item > 2)
console.log(filterResult) // 3,4,5,4,3
Array Boolean Filter
Array.every(filer).Array.some(filer).
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
const everyResult = numbers.every((item, index, array) => item > 2)
const someResult = numbers.some((item, index, array) => item > 2)
console.log(everyResult) // false
console.log(someResult) // true
Array With
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
console.log(arr.with(2, 6)) // [1, 2, 6, 4, 5]
console.log(arr) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
console.log(arr.with(2, 6).map(x => x ** 2)) // [1, 4, 36, 16, 25]
const frameworks = ['Nuxt', 'Remix', 'SvelteKit', 'Ember']
console.log(frameworks.with(-1, 'React'))
// ✅ Returns a copy with the change: ['Nuxt', 'Remix', 'SvelteKit', 'React'].
Array Map
相当于 Haskell 中的 List Map:
;[].map(item => item + 1) // map over
Array Flat
[2, [2, 2]] => [2, 2, 2]
Array FlatMap
map + flat.
function flattenDeep(arr) {
return Array.isArray(arr)
? arr.reduce((a, b) => a.concat(flattenDeep(b)), [])
: [arr]
}
flattenDeep([1, [[2], [3, [4]], 5]])
// => [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
// ES2019
;[1, [2, [3, [4]], 5]].flat(Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY)
// => [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
function flattenDeep(arr) {
return arr.flatMap((subArray, index) =>
Array.isArray(subArray) ? flattenDeep(subArray) : subArray
)
}
flattenDeep([1, [[2], [3, [4]], 5]])
// => [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Array Reduce
reduce/reduceRight:
- Accumulator: initial value, otherwise
array[0]. - Current value:
array[0], otherwisearray[1]. - Implement array sets manipulation (
reduce/filter/includes). - Implement
XXXByfunctional methods.
;[].reduce(
(previous, current, currentIndex, arr) => current + previous,
initial
) // fold function
Implement groupBy:
const groupByLength = ['one', 'two', 'three'].reduce(
(acc, current, _index, _array) => {
const key = current.length
;(acc[key] || (acc[key] = [])).push(current)
return acc
},
{}
)
// {3: ["one", "two"], 5: ["three"]}
const groupByFunction = [1.3, 2.1, 2.4].reduce(
(acc, current, _index, _array) => {
const key = Math.floor(current)
;(acc[key] || (acc[key] = [])).push(current)
return acc
},
{}
)
// {1: [1.3], 2: [2.1, 2.4]}
Array Traversal
array.forEach((val) => {}) // 遍历数组所有元素.
Array Sort
toExchange:
return 1: a, b 交换位置.return -1: a, b 不交换位置.
arr.sort(toExchange)
strings.sort((a, b) => a.localeCompare(b))
strings.sort((a, b) => new Intl.Collator('en').compare(a, b))
Array Reverse
;[].reverse()
// Tips
// 反转字符串
const reverseStr = normalizedStr.split('').reverse().join('')
Array Spread
- Shallow Clone.
- Iterable Consumer.
arr2.push(...arr1)
const obj = { x: 1, y: 2, z: 3 }
obj[Symbol.iterator] = function* () {
yield 1
yield 2
yield 3
}
const array = [...obj] // print [1, 2, 3]
Array Deep Clone
const nestedArray = [1, [2], 3]
const arrayCopy = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(nestedArray))
// Make some changes
arrayCopy[0] = '1' // change shallow element
arrayCopy[1][0] = '3' // change nested element
console.log(arrayCopy) // [ '1', [ '3' ], 3 ]
// Good: Nested array NOT affected
console.log(nestedArray) // 1, [ 2 ], 3 ]
Typed Array
Typed Array
是 ArrayBuffer (用于 Web GL 高效率内存操作) 其中一种视图:
- File.
- XMLHttpRequest.
- Fetch.
- Web Worker.
- WebSocket.
- Canvas.
- WebGL.
- Web Audio.
// 第一个参数是应该返回的数组类型
// 其余参数是应该拼接在一起的定型数组
function typedArrayConcat(TypedArrayConstructor, ...typedArrays) {
// 计算所有数组中包含的元素总数
const numElements = typedArrays.reduce((x, y) => (x.length || x) + y.length)
// 按照提供的类型创建一个数组, 为所有元素留出空间
const resultArray = new TypedArrayConstructor(numElements)
// 依次转移数组
let currentOffset = 0
typedArrays.forEach((x) => {
resultArray.set(x, currentOffset)
currentOffset += x.length
})
return resultArray
}
const concatArray = typedArrayConcat(
Int32Array,
Int8Array.of(1, 2, 3),
Int16Array.of(4, 5, 6),
Float32Array.of(7, 8, 9)
)
console.log(concatArray) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
console.log(concatArray instanceof Int32Array) // true
const view = new Int16Array([25, 50])
console.log(view instanceof Int16Array) // true
// eslint-disable-next-line unicorn/no-instanceof-array
console.log(view instanceof Array) // false
console.log(Array.isArray(view)) // false
Map
size.has().get().set().delete().clear().keys().values().entries().
const map = new Map([
// You define a map via an array of 2-element arrays. The first
// element of each nested array is the key, and the 2nd is the value
['name', 'Jean-Luc Picard'],
['age', 59],
['rank', 'Captain'],
])
// To get the value associated with a given `key` in a map, you
// need to call `map.get(key)`. Using `map.key` will **not** work.
map.get('name') // 'Jean-Luc Picard'
const map = new Map([])
// eslint-disable-next-line no-new-wrappers, unicorn/new-for-builtins
const n1 = new Number(5)
// eslint-disable-next-line no-new-wrappers, unicorn/new-for-builtins
const n2 = new Number(5)
map.set(n1, 'One')
map.set(n2, 'Two')
// `n1` and `n2` are objects, so `n1 !== n2`. That means the map has
// separate keys for `n1` and `n2`.
map.get(n1) // 'One'
map.get(n2) // 'Two'
map.get(5) // undefined
// If you were to do this with an object, `n2` would overwrite `n1`
const obj = {}
obj[n1] = 'One'
obj[n2] = 'Two'
const two1 = obj[n1] // 'Two'
const two2 = obj[5] // 'Two'
const objectClone = new Map(Object.entries(object))
const arrayClone = new Map(Array.from(map.entries))
const map = new Map([
['name', 'Jean-Luc Picard'],
['age', 59],
['rank', 'Captain'],
])
// The `for/of` loop can loop through iterators
for (const key of map.keys())
console.log(key) // 'name', 'age', 'rank'
for (const value of map.values())
console.log(value) // 'Jean-Luc Picard', 59, 'Captain'
for (const [key, value] of map.entries()) {
console.log(key) // 'name', 'age', 'rank'
console.log(value) // 'Jean-Luc Picard', 59, 'Captain'
}
Set
size.has().add().delete().clear().keys().values().entries().
class XSet extends Set {
union(...sets) {
return XSet.union(this, ...sets)
}
intersection(...sets) {
return XSet.intersection(this, ...sets)
}
difference(set) {
return XSet.difference(this, set)
}
symmetricDifference(set) {
return XSet.symmetricDifference(this, set)
}
cartesianProduct(set) {
return XSet.cartesianProduct(this, set)
}
powerSet() {
return XSet.powerSet(this)
}
// 返回两个或更多集合的并集
// new Set([...setA, ...setB]);
static union(a, ...bSets) {
const unionSet = new XSet(a)
for (const b of bSets) {
for (const bValue of b)
unionSet.add(bValue)
}
return unionSet
}
// 返回两个或更多集合的交集
// new Set([...setA].filter(x => setB.has(x)))
static intersection(a, ...bSets) {
const intersectionSet = new XSet(a)
for (const aValue of intersectionSet) {
for (const b of bSets) {
if (!b.has(aValue))
intersectionSet.delete(aValue)
}
}
return intersectionSet
}
// 返回两个集合的差集
// new Set([...setA].filter(x => !setB.has(x)))
static difference(a, b) {
const differenceSet = new XSet(a)
for (const bValue of b) {
if (a.has(bValue))
differenceSet.delete(bValue)
}
return differenceSet
}
// 返回两个集合的对称差集
static symmetricDifference(a, b) {
// 按照定义, 对称差集可以表达为:
return a.union(b).difference(a.intersection(b))
}
// 返回两个集合 (数组对形式) 的笛卡儿积
// 必须返回数组集合, 因为笛卡儿积可能包含相同值的对
static cartesianProduct(a, b) {
const cartesianProductSet = new XSet()
for (const aValue of a) {
for (const bValue of b)
cartesianProductSet.add([aValue, bValue])
}
return cartesianProductSet
}
// 返回一个集合的幂集
static powerSet(a) {
const powerSet = new XSet().add(new XSet())
for (const aValue of a) {
for (const set of new XSet(powerSet))
powerSet.add(new XSet(set).add(aValue))
}
return powerSet
}
}
WeakMap and WeakSet
WeakMap 结构与 Map 结构基本类似, 唯一的区别就是 WeakMap 只接受非 null 对象作为键名:
- 弱键: 键名构建的引用无法阻止对象执行垃圾回收.
- 不可迭代键: 键/值随时可能被垃圾回收, 无需提供迭代能力, 无
clear()方法.
它的键所对应的对象可能会在将来消失. 一个对应 DOM 元素的 WeakMap 结构, 当某个 DOM 元素被清除, 其所对应的 WeakMap 记录就会自动被移除.
有时候我们会把对象作为一个对象的键用来存放属性值, 普通集合类型比如简单对象 (Object/Map/Set) 会阻止垃圾回收器对这些作为属性键存在的对象的回收, 有造成内存泄漏的危险, WeakMap/WeakSet 则更加内存安全:
- Caching computed results.
- Managing listeners.
- Keeping private data.
Date
const now = new Date()
now.getFullYear() // 1-n
now.getMonth() // Warn: 0-11
now.getDate() // 1-n
now.getDay() // Warn: 0-6
now.getHours()
now.getSeconds()
now.toString()
now.toDateString()
now.toTimeString()
now.toUTCString()
now.toLocaleString()
now.toLocaleDateString()
now.toLocaleTimeString()
function daysOfMonth(year, month) {
// `0` for last month of next month
return new Date(year, month + 1, 0).getDate()
}
function prevYear(year) {
return new Date(year - 1, 0).getFullYear()
}
function nextYear(year) {
return new Date(year + 1, 0).getFullYear()
}
function prevMonth(year, month) {
return new Date(year, month - 1).getMonth()
}
function nextMonth(year, month) {
return new Date(year, month + 1).getMonth()
}
function getDateItemList(year, month) {
const days = daysOfMonth(year, month)
const currentDateItemList = [...Array.from({ length: days }).keys()].map((index) => {
return DateItem(year, month, 1 + index)
})
const firstDayItem = DateItem(year, month, 1)
const firstDayWeekday = firstDayItem.day
const lastMonthDays = daysOfMonth(year, month - 1)
const prefixDays = firstDayWeekday === 0 ? 7 : firstDayWeekday
const prefixFirstDay = lastMonthDays - prefixDays + 1
const prefixYear = prevYear(year)
const prefixMonth = prevMonth(year, month)
const prefixDateItemList = [...Array.from({ length: prefixDays }).keys()].map((index) => {
return DateItem(prefixYear, prefixMonth, prefixFirstDay + index)
})
const lastDayItem = DateItem(year, month, days)
const lastDayWeekday = lastDayItem.day
const suffixDays = lastDayWeekday === 6 ? 7 : 6 - lastDayWeekday
const suffixYear = nextYear(year)
const suffixMonth = nextMonth(year, month)
const suffixDateItemList = [...Array.from({ length: suffixDays }).keys()].map((index) => {
return DateItem(suffixYear, suffixMonth, 1 + index)
})
const dateItemList = [
...prefixDateItemList,
...currentDateItemList,
...suffixDateItemList,
]
return dateItemList
}
Temporal
Temporal Basis
Temporal.ZonedDateTime.from({
year,
month,
day,
timeZone: Temporal.Now.timeZone(),
})
Temporal.ZonedDateTime.from({
year,
month,
day,
hour,
minute,
timeZone: Temporal.Now.timeZone(),
})
const second = Temporal.Now.zonedDateTimeISO().second
const hour = Temporal.Now.zonedDateTimeISO().hour
const day = Temporal.Now.zonedDateTimeISO().day
Temporal.Now.zonedDateTimeISO().with({ second: 30 })
Temporal.Now.zonedDateTimeISO().with({ hour: 13 })
Temporal.Now.zonedDateTimeISO().with({ day: 1 })
Temporal.Now.zonedDateTimeISO().withPlainTime(
new Temporal.PlainTime(23, 59, 59, 999, 999, 999)
)
Temporal Range
const dayOfWeek = Temporal.Now.zonedDateTimeISO().dayOfWeek
const dayOfYear = Temporal.Now.zonedDateTimeISO().dayOfYear
const daysInMonth = new Temporal.PlainYearMonth(2012, 2).daysInMonth
const daysInMonth = Temporal.PlainYearMonth.from('2012-02').daysInMonth
const weekOfYear = Temporal.Now.zonedDateTimeISO().weekOfYear
const weekOfYear = Temporal.PlainDate.from({
day: 31,
month: 12,
year: Temporal.Now.plainDateISO(),
}).weekOfYear
const inLeapYear = Temporal.PlainDate.from('2000-01-01').inLeapYear
Temporal.Now.zonedDateTimeISO().add(Temporal.Duration.from({ days: 7 }))
Temporal.Now.zonedDateTimeISO().subtract(Temporal.Duration.from({ days: 14 }))
Temporal.Now.zonedDateTimeISO()
.with({ month: 1, day: 1 })
.add(Temporal.Duration.from({ days: 256 }))
Temporal.Now.zonedDateTimeISO()
.with({ month: 1, day: 1 })
.add(Temporal.Duration.from({ weeks: 23 }))
Temporal.Instant.fromEpochMilliseconds(Math.max.apply(null, dateArrays))
Temporal.Instant.fromEpochMilliseconds(Math.min.apply(null, dateArrays))
Temporal Display
new Intl.DateTimeFormat('en-GB', {
dateStyle: 'full',
timeStyle: 'medium',
}).format(Temporal.Now.zonedDateTimeISO())
new Intl.DateTimeFormat('de-DE', { weekday: 'short', hour: 'numeric' }).format(
Temporal.Now.zonedDateTimeISO()
)
Temporal.PlainDate.from('2007-01-27').until('2007-01-29')
Temporal.PlainDate.from('2007-01-27')
.since('2007-01-29')
.total({ unit: 'millisecond' })
Temporal.PlainDate.from('2007-01-27').since('2007-01-29').total({ unit: 'day' })
Temporal Query
const isBefore = Temporal.PlainDate.compare('2010-10-20', '2010-10-21') === -1
const isAfter = Temporal.PlainDate.compare('2010-10-20', '2010-10-19') === 1
const isEqual = Temporal.PlainDate.from('2010-10-20').equals('2010-10-21')
const isEqual = Temporal.PlainDate.from('2010-10-20').equals('2010-10-20')
const isEqual
= Temporal.PlainDate.from('2010-10-20').month
=== Temporal.PlainDate.from('2010-10-21').month
const isPlainTime = Temporal.Now.plainTimeISO() instanceof Temporal.PlainTime
const isPlainDate = Temporal.Now.plainDateISO() instanceof Temporal.PlainDate
const isPlainDateTime
= Temporal.Now.plainDateTimeISO() instanceof Temporal.PlainDateTime
const isZonedDateTime
= Temporal.Now.zonedDateTimeISO() instanceof Temporal.ZonedDateTime
Variable
Variable Hoisting
- 一方面规定,
var/function声明的全局变量, 依旧是全局对象的属性, 意味着会Hoisting. - 另一方面规定,
let/const/class声明的全局变量, 不属于全局对象的属性, 意味着不会Hoisting. var只有函数作用域,let/const拥有块级作用域.var表达式和function声明都将会被提升到当前作用域 (全局作用域/函数作用域) 顶部, 其余表达式顺序不变.
| Hoisting | Scope | Creates Global Properties | |
|---|---|---|---|
var | Declaration | Function | Yes |
let | Temporal dead zone | Block | No |
const | Temporal dead zone | Block | No |
class | Temporal dead zone | Block | No |
function | Complete | Block | Yes |
import | Complete | Module-global | No |
// 我们知道这个行不通 (假设没有未定义的全局变量)
function example() {
console.log(notDefined) // => throws a ReferenceError
}
// 在引用变量后创建变量声明将会因变量提升而起作用.
// 注意: 真正的值 `true` 不会被提升.
function example() {
console.log(declaredButNotAssigned) // => undefined
var declaredButNotAssigned = true
}
// 解释器将变量提升到函数的顶部
// 这意味着我们可以将上边的例子重写为:
function example() {
let declaredButNotAssigned
console.log(declaredButNotAssigned) // => undefined
declaredButNotAssigned = true
}
// 使用 const 和 let
function example() {
console.log(declaredButNotAssigned) // => throws a ReferenceError
console.log(typeof declaredButNotAssigned) // => throws a ReferenceError
const declaredButNotAssigned = true
}
function example() {
console.log(named) // => undefined
named() // => TypeError named is not a function
superPower() // => ReferenceError superPower is not defined
var named = function superPower() {
console.log('Flying')
}
}
Let Variable
- 块级作用域内定义的变量/函数, 在块级作用域外 ReferenceError.
- 不存在变量提升, 导致暂时性死区 (Temporal Dead Zone).
letvariable infor-loopclosure, every closure for each loop binds the block-scoped variable.
const a = 1
b = 3 // temporal dead zone: throw reference error
let b = 2
let 变量拥有块级作用域 (每个 setTimeout 引用的都是不同的变量实例):
// for (var i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
// setTimeout(() => console.log(i), 0);
// }
// Output 5, 5, 5, 5, 5.
// 所有的 i 都是同一个变量, 输出同一个最终值.
for (let i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
setTimeout(() => console.log(i), 0)
// Output: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4.
// JavaScript 引擎会为每个迭代循环声明一个新的迭代变量.
// 每个 setTimeout 引用的都是不同的变量实例.
Const Variable
- const 一旦声明变量, 就必须立即初始化, 不能留到以后赋值.
- 引用一个
Reference变量时, 只表示此变量地址不可变, 但所引用变量的值/属性可变 (xxx *const, 即const指针, 指向一个变量). - 块级作用域.
- 不存在变量提升, 导致暂时性死区 (Temporal Dead Zone).
const f = () => g()
const g = () => 123
// We call f() after g() was declared:
assert.equal(f(), 123)
funcDecl()
const MY_STR = 'abc'
function funcDecl() {
assert.throws(() => MY_STR, ReferenceError)
}
Type Detection
function typeOf(o) {
const _toString = Object.prototype.toString
const _type = {
'undefined': 'undefined',
'number': 'number',
'boolean': 'boolean',
'string': 'string',
'[object Function]': 'function',
'[object GeneratorFunction]': 'function',
'[object Array]': 'array',
'[object Date]': 'date',
'[object RegExp]': 'regexp',
'[object Error]': 'error',
'[object JSON]': 'json',
}
return _type[typeof o] || _type[_toString.call(o)] || (o ? 'object' : 'null')
}
function type(item) {
const reTypeOf = /^\[object\s(.*?)\]$/
return Object.prototype.toString
.call(item)
.replace(reTypeOf, '$1')
.toLowerCase()
}
Null Detection
不应使用 typeof 检测 null, 应使用 ===/!==.
/*
* ECMAScript 标准的重大 bug
*/
const objectType = typeof null // => object
Property Detection
- 由于属性值可能为零值值表达式, 不应使用零值表达式(
0/NaN/''/null/undefined) 检测属性值. - 应使用
for in进行属性检测.
Custom Object Detection
object instanceof Constructor: 在原型链上查找构造器的原型对象 (Constructor.prototype).prop in object: 查找原型链属性名.
/**
* L 表示左表达式, R 表示右表达式: L 为变量, R 为类型.
*/
function instanceOf(L, R) {
const prototype = R.prototype
let chain = L[[proto]]
while (true) {
if (chain === null)
return false
if (prototype === chain)
return true
chain = chain[[proto]]
}
}
Type Conversion
Type Conversion Context
- 字符串 -> 整数:
+string/Number(string)/parseInt(string, arg1). - any ->
bool:!!any. - const ->
object:(const). parseInt(str, base):- 遇到非数字字符立即停止运行, 返回当前转化值.
- 将 0 开头字符串解析为八进制数, 0x 开头字符串解析为十六进制数.
boolean在数值运算环境中 true => 1, false => 0.数组在数值运算环境中转化为 0 (空数组)/num (单一元素数组)/NaN (多元素数组/NaN 数组).对象在逻辑运算环境中转化为 true , 包括 false 的封装对象.对象在数值运算环境中先利用 valueOf(object), 再利用 toString() 转化为数字, 若转化失败, 则返回 NaN.对象与数值加号运算: 先数值加, (失败后)再字符串加.
// good
const totalScore = String(this.reviewScore)
// good
const val = Number(inputValue)
// good
const val = Number.parseInt(inputValue, 10)
// good
const hasAge = Boolean(age)
// best
const hasAge = !!age
Type Conversion Algorithms
function ToString(argument) {
if (argument === undefined) {
return 'undefined'
} else if (argument === null) {
return 'null'
} else if (argument === true) {
return 'true'
} else if (argument === false) {
return 'false'
} else if (TypeOf(argument) === 'number') {
return Number.toString(argument)
} else if (TypeOf(argument) === 'string') {
return argument
} else if (TypeOf(argument) === 'symbol') {
return Symbol.toString(argument)
} else if (TypeOf(argument) === 'bigint') {
return BigInt.toString(argument)
} else {
// argument is an object
const primValue = ToPrimitive(argument, 'string')
return ToString(primValue)
}
}
function ToPropertyKey(argument) {
const key = ToPrimitive(argument, 'string') // (A)
if (TypeOf(key) === 'symbol')
return key
return ToString(key)
}
function ToNumeric(value) {
const primValue = ToPrimitive(value, 'number')
if (TypeOf(primValue) === 'bigint')
return primValue
return ToNumber(primValue)
}
function ToNumber(argument) {
if (argument === undefined) {
return Number.NaN
} else if (argument === null) {
return +0
} else if (argument === true) {
return 1
} else if (argument === false) {
return +0
} else if (TypeOf(argument) === 'number') {
return argument
} else if (TypeOf(argument) === 'string') {
return parseTheString(argument) // not shown here
} else if (TypeOf(argument) === 'symbol') {
throw new TypeError('Failed!')
} else if (TypeOf(argument) === 'bigint') {
throw new TypeError('Failed!')
} else {
// argument is an object
const primValue = ToPrimitive(argument, 'number')
return ToNumber(primValue)
}
}
ToPrimitive:
[Symbol.toPrimitive]().toString().valueOf().
/**
* @param input input string
* @param hint Which type is preferred for the result string, number etc.
*/
function ToPrimitive(
input: any,
hint: 'string' | 'number' | 'default' = 'default'
) {
if (TypeOf(input) === 'object') {
const exoticToPrim = input[Symbol.toPrimitive] // (A)
if (exoticToPrim !== undefined) {
const result = exoticToPrim.call(input, hint)
if (TypeOf(result) !== 'object')
return result
throw new TypeError('[Symbol.toPrimitive]() failed!')
}
if (hint === 'default')
hint = 'number'
return OrdinaryToPrimitive(input, hint)
} else {
// input is already primitive
return input
}
}
function OrdinaryToPrimitive(O: object, hint: 'string' | 'number') {
const methodNames
= hint === 'string' ? ['toString', 'valueOf'] : ['valueOf', 'toString']
for (const name of methodNames) {
const method = O[name]
if (IsCallable(method)) {
const result = method.call(O)
if (TypeOf(result) !== 'object')
return result
}
}
throw new TypeError('Conversion failed!')
}
Operators
Loose Comparison
== 与 != loose comparison:
- Type conversion first, then comparison.
- Return comparison between
ToNumber(x)andToPrimitive(y).
/** Loose equality (==) */
function abstractEqualityComparison(x, y) {
if (TypeOf(x) === TypeOf(y)) {
// Use strict equality (===)
return strictEqualityComparison(x, y)
}
// Comparing null with undefined
if (x === null && y === undefined)
return true
if (x === undefined && y === null)
return true
// Comparing a number and a string
if (TypeOf(x) === 'number' && TypeOf(y) === 'string')
return abstractEqualityComparison(x, Number(y))
if (TypeOf(x) === 'string' && TypeOf(y) === 'number')
return abstractEqualityComparison(Number(x), y)
// Comparing a bigint and a string
if (TypeOf(x) === 'bigint' && TypeOf(y) === 'string') {
const n = StringToBigInt(y)
if (Number.isNaN(n))
return false
return abstractEqualityComparison(x, n)
}
if (TypeOf(x) === 'string' && TypeOf(y) === 'bigint')
return abstractEqualityComparison(y, x)
// Comparing a boolean with a non-boolean
if (TypeOf(x) === 'boolean')
return abstractEqualityComparison(Number(x), y)
if (TypeOf(y) === 'boolean')
return abstractEqualityComparison(x, Number(y))
// Comparing an object with a primitive
// (other than undefined, null, a boolean)
if (
['string', 'number', 'bigint', 'symbol'].includes(TypeOf(x))
&& TypeOf(y) === 'object'
) {
return abstractEqualityComparison(x, ToPrimitive(y))
}
if (
TypeOf(x) === 'object'
&& ['string', 'number', 'bigint', 'symbol'].includes(TypeOf(y))
) {
return abstractEqualityComparison(ToPrimitive(x), y)
}
// Comparing a bigint with a number
if (
(TypeOf(x) === 'bigint' && TypeOf(y) === 'number')
|| (TypeOf(x) === 'number' && TypeOf(y) === 'bigint')
) {
if (
[Number.NaN, +Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY, Number.NEGATIVE_INFINITY].includes(x)
|| [Number.NaN, +Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY, Number.NEGATIVE_INFINITY].includes(y)
) {
return false
}
if (isSameMathematicalValue(x, y))
return true
else
return false
}
return false
}
Strict Comparison
=== 与 !==:
- Strings: same length, same characters in corresponding positions.
- Numbers: numerically equal.
- Objects: refer to same Object.
- Positive and negative
0are equal to one another. NaNis not equal to anything, includingNaN.nullandundefinedtypes are not equal with===, but equal with==.
const true1 = 0 == false // true
const false1 = 0 === false // false
const true2 = 1 == '1' // true
const false2 = 1 === '1' // false
const true3 = undefined == null // true
const false3 = undefined === null // false
const true4 = '0' == false // true
const false4 = '0' === false // false
// eslint-disable-next-line no-self-compare
const false5 = [] == [] // false, refer different objects in memory
// eslint-disable-next-line no-self-compare
const false6 = [] === [] // false, refer different objects in memory
// eslint-disable-next-line no-self-compare
const false7 = {} == {} // false, refer different objects in memory
// eslint-disable-next-line no-self-compare
const false8 = {} === {} // false, refer different objects in memory
Object.is:
// Case 1: Evaluation result is the same as using ===
Object.is(25, 25) // true
Object.is('foo', 'foo') // true
Object.is('foo', 'bar') // false
Object.is(null, null) // true
Object.is(undefined, undefined) // true
Object.is(window, window) // true
Object.is([], []) // false
const foo = { a: 1 }
const bar = { a: 1 }
Object.is(foo, foo) // true
Object.is(foo, bar) // false: different reference pointers.
// Case 2: Signed zero
Object.is(0, -0) // false
Object.is(+0, -0) // false
Object.is(-0, -0) // true
Object.is(0n, -0n) // true
// Case 3: NaN
Object.is(Number.NaN, 0 / 0) // true
Object.is(Number.NaN, Number.NaN) // true
if (!Object.is) {
Object.defineProperty(Object, 'is', {
value: (x, y) => {
// SameValue algorithm
if (x === y) {
// return true if x and y are not 0, OR
// if x and y are both 0 of the same sign.
// This checks for cases 1 and 2 above.
return x !== 0 || 1 / x === 1 / y
} else {
// return true if both x AND y evaluate to NaN.
// The only possibility for a variable to not be strictly equal to itself
// is when that variable evaluates to NaN (example: Number.NaN, 0/0, NaN).
// This checks for case 3.
// eslint-disable-next-line no-self-compare
return x !== x && y !== y
}
},
})
}
Conditional Expression
养成使用分号结束句子的习惯, 需分行显示的语句必须确保单行不会形成完整语义:
const i = a ? 1 : b ? 2 : c ? 3 : 4
Add Operator
a + b:
- 如果有一个是对象, 则遵循对象对原始值的转换过程:
- Date 对象直接调用 toString 完成转换.
- 其他对象通过 valueOf 转化, 如果转换不成功则调用 toString.
- 如果两个都是对象, 两个对象都遵循步骤 1 转换到字符串.
- 两个数字, 进行算数运算.
- 两个字符串, 直接拼接.
- 一个字符串一个数字, 直接拼接为字符串.
Dot Operator
. 优先级高于 =:
el.data 优先求值, 引用 old, 指向 old.data.
5 => el, 5 => el.data (old.data).
let el = { data: 1 }
const old = el
el.data = el = 5
console.log(el) // 5
console.log(el.data) // undefined
console.log(old) // { data: 5 }
console.log(old.data) // 5
Logical Operator
- Optional Chaining Operator
?.: Legible property chains that don't throw an error if a requested reference is missing. - Nullish coalescing operator
??: Binary operator. If the value of left side expression isnullorundefined, right side of the operator is evaluated. - Logical assignment operators:
&&=,||=,??=.
| Assignment Operator | Equivalent To | Only Assigns When a |
|---|---|---|
a ||= b | a || (a = b) | Falsy |
a &&= b | a && (a = b) | Truthy |
a ??= b | a ?? (a = b) | Nullish |
Delete Operator
delete operator returns a boolean value:
trueon a successful deletion.falseon a failed deletion:var/let/constvariables cannot be deleted usingdeleteoperator.
const name = 'Lydia'
age = 21
// eslint-disable-next-line no-delete-var
console.log(delete name) // false
// eslint-disable-next-line no-delete-var
console.log(delete age) // true
Operator Reference
Destructuring Pattern Matching
- 建议只要有可能, 就不要在模式中放置圆括号.
- 赋值语句的非模式部分, 可以使用圆括号.
- Every time access value via
.: stop and think whether use destructuring instead. - Destructure as early as possible.
- Remember to include default values, especially in nested destructuring.
Destructuring Default Value
- ES6 内部使用严格相等运算符 (===), 判断一个位置是否有值. 若此位置无值, 则使用默认值.
- 如果一个数组成员不严格等于 undefined, 默认值不会生效.
const [x = 1] = [undefined]
console.log(x) // 1
const [x = 1] = [null]
console.log(x) // null
let [x = 1, y = x] = [] // x=1; y=1
let [x = 1, y = x] = [2] // x=2; y=2
let [x = 1, y = x] = [1, 2] // x=1; y=2
let [x = y, y = 1] = [] // ReferenceError
Object Destructuring
- 解构赋值的规则: 只要等号右边的值不是对象, 就先将其转为对象.
undefined/null无法转化为对象:
const { prop: x } = undefined // TypeError
const { prop: y } = null // TypeError
const { bar, foo } = { foo: 'aaa', bar: 'bbb' }
console.log(foo) // "aaa"
console.log(bar) // "bbb"
const { baz } = { foo: 'aaa', bar: 'bbb' }
console.log(baz) // undefined
- 真正被赋值的是后者, 而不是前者:
const { foo: baz } = { foo: 'aaa', bar: 'bbb' }
console.log(baz) // "aaa"
const { first: f, last: l } = { first: 'hello', last: 'world' }
console.log(f) // 'hello'
console.log(l) // 'world'
- Left-hand side of a normal assignment:
const obj = {}
;[first, ...obj.prop] = ['a', 'b', 'c']
// first = 'a'; obj.prop = ['b', 'c']
const arr = []
;({ bar: arr[0] } = { bar: true })
console.log(arr) // [true]
JSON Object Destructuring
const jsonData = {
id: 42,
status: 'OK',
data: [867, 5309],
}
const { id, status, data: number } = jsonData
console.log(id, status, number)
// 42, "OK", [867, 5309]
Import Destructuring
const { SourceMapConsumer, SourceNode } = require('source-map')
Number and Boolean Destructuring
number/boolean 会自动构造原始值包装对象:
let { toString: s } = 123
const truthy = s === Number.prototype.toString // true
let { toString: s } = true
const truthy = s === Boolean.prototype.toString // true
Iterator Destructuring
等号右��边必须为数组等实现了 Iterator 接口的对象, 否则报错:
- Array.
- Set.
- Generator function.
const [foo, [[bar], baz]] = [1, [[2], 3]]
console.log(foo) // 1
console.log(bar) // 2
console.log(baz) // 3
const [, , third] = ['foo', 'bar', 'baz']
console.log(third) // "baz"
const [x, , y] = [1, 2, 3]
console.log(x) // 1
console.log(y) // 3
const [head, ...tail] = [1, 2, 3, 4]
console.log(head) // 1
console.log(tail) // [2, 3, 4]
const [x, y, ...z] = ['a']
console.log(x) // "a"
console.log(y) // undefined
console.log(z) // []
// Generator 函数
function* fibs() {
let a = 0
let b = 1
while (true) {
yield a
;[a, b] = [b, a + b]
}
}
const [first, second, third, fourth, fifth, sixth] = fibs()
console.log(sixth) // 5
- Left-hand side of a normal assignment:
let x = 1
let y = 2
;[x, y] = [y, x]
Map and List Destructuring
for index in Iterable<T>: key.for [key, value] of Iterable<T>: entry.
const map = new Map()
map.set('first', 'hello')
map.set('second', 'world')
for (const [key, value] of map)
console.log(`${key} is ${value}`)
// first is hello
// second is world
// 获取键名
for (const [key] of map) {
// ...
}
// 获取键值
for (const [, value] of map) {
// ...
}
String Destructuring
const [a, b, c, d, e] = 'hello'
console.log(a) // "h"
console.log(b) // "e"
console.log(c) // "l"
console.log(d) // "l"
console.log(e) // "o"
const { length: len } = 'hello'
console.log(len) // 5
Function Parameters Destructuring
- 可用于工厂 (
factory) / 设置 (options) 模式传参一般为options对象, - 具有固定的属性名.
- 一次性定义多个参数.
- 一次性定义多个参数的默认值.
// 参数是一组有次序的值
function f1([x, y, z]) {}
f1([1, 2, 3])
// 参数是一组无次序的值
function f2({ x, y, z }) {}
f2({ z: 3, y: 2, x: 1 })
// 可省略 const foo = config.foo || 'default foo';
jQuery.ajax = function (
url,
{
async = true,
beforeSend = function () {},
cache = true,
complete = function () {},
crossDomain = false,
global = true,
// ... more config
}
) {
// ... do stuff
}
Function Return Value Destructuring
返回多个值:
// 返回一个数组
function example1() {
return [1, 2, 3]
}
const [a, b, c] = example1()
// 返回一个对象
function example2() {
return {
foo: 1,
bar: 2,
}
}
const { foo, bar } = example2()
Control Flow
Switch Case Statement
用 Strategy Pattern 代替 switch/case 语句:
function doAction(action) {
const actions = {
hack() {
return 'hack'
},
slash() {
return 'slash'
},
run() {
return 'run'
},
}
if (typeof actions[action] !== 'function')
throw new TypeError('Invalid action.')
// 闭包方法集
return actions[action]()
}
Object
OOP Features
共用方法, 单独属性, 封装细节:
- 原型代理 (享元模式): 利用享元模式共享公有属性与通用方法.
- 实例状态 (原型克隆): 利用原型克隆拥有各自属性值.
- 封装性 (闭包式继承): 利用闭包方法实现属性私有化.
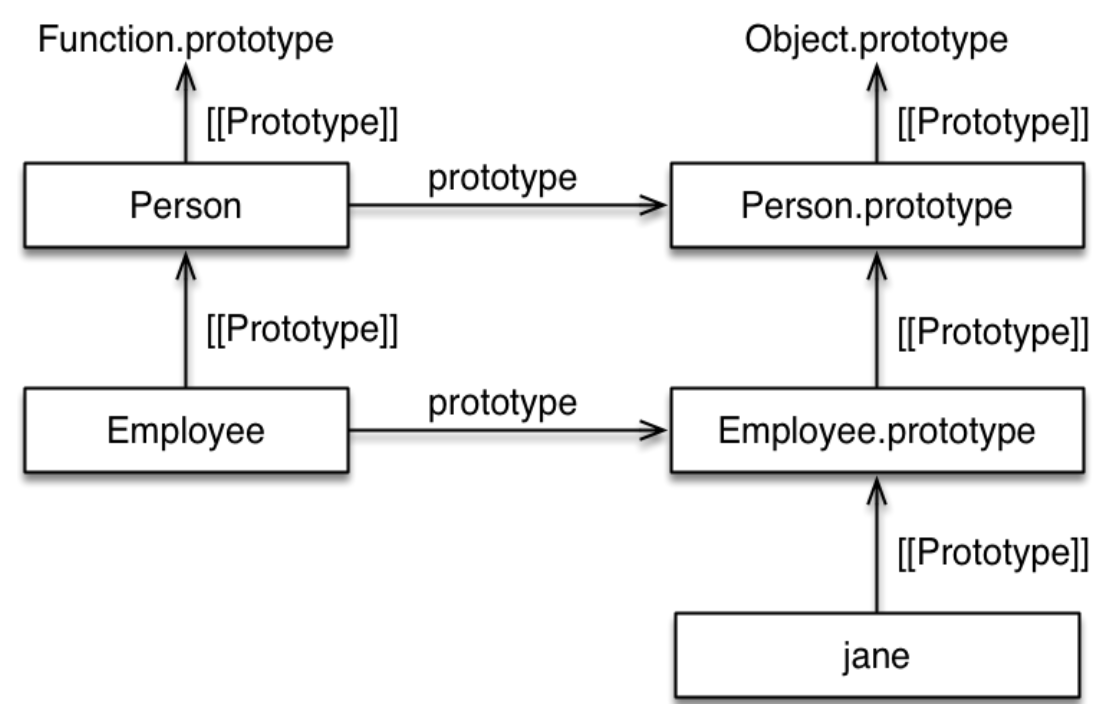
Prototype Chain
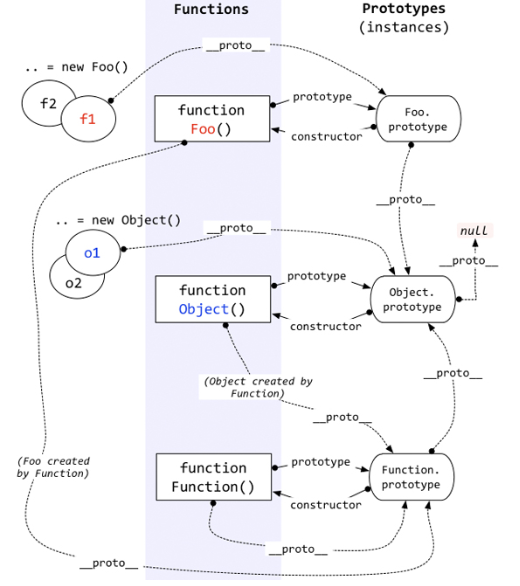
- 实例化对象仅有属性
__proto__, 没有属性prototype, 函数才具有属性prototype(指向引擎为其自动创建的原型对象):Instance.__proto__ === Constructor.prototype. - 所有引用类型 (包括对象/数组/函数/构造函数) 都有属性
__proto__(隐式原型). - 所有函数/构造函数的
__proto__都指向Function.prototype. - 除
Object.prototype.__proto__指向 null 外, 其余函数/构造函数的原型对象的__proto__都指向Object.prototype. - 除
Object.create()外, 所新建对象的__proto__指向构造该对象的构造函数的原型对象(prototype). - 除
typeof Function.prototype为 'function' 外, 其余函数/构造函数的原型对象都为 '对象'(typeof为 'object'). - 先有
Object.prototype(原型链顶端),Function.prototype继承Object.prototype而产生, 最后Object/Function/Array/其它构造函数继承Function.prototype而产生.
// True because of `Object` is `function Object()` and inherited from `Function.prototype`
// Object has its own `prototype` property refer to `Object.prototype`
const truthy = Object[[proto]] === Function.prototype
// True because of `Array` is `function Array()` and inherited from `Function.prototype`
// Array has its own `prototype` property refer to `Array.prototype`
const truthy = Array[[proto]] === Function.prototype
// True because of Function is `function Function()` and inherited from `Function.prototype`
// Function has its own `prototype` property refer to `Function.prototype`
const truthy = Function[[proto]] === Function.prototype
// True because of Object.prototype is the top of inheritance chains (null is Object.prototype.__proto__)
// all `object/function/array instance`.__proto__......__proto__ refer to Object.prototype
const truthy = Function[[proto]][[proto]] === Object.prototype
// True:
const truthy = Object instanceof Function
const truthy = Function instanceof Object
Object.__proto__->Function.prototype.Function.prototype.__proto__->Object.prototype.Object.prototype.__proto__->null.
__proto__:
[[proto]]getter isObject.getPrototypeOf(object).[[proto]]setter isObject.setPrototypeOf(object, prototype).
function Foo(value) {
this.val = value
}
// Auto create FooPrototype
// Foo.prototype -> FooPrototype
// FooPrototype.constructor -> [function Foo]
// foo.__proto__ -> FooPrototype
const foo = new Foo(2)
function Person() {}
const person1 = new Person()
const person2 = new Person()
console.log(person1 !== Person) // true
console.log(person1 !== Person.prototype) // true
console.log(Person.prototype !== Person) // true
// eslint-disable-next-line no-proto, no-restricted-properties
console.log(person1.__proto__ === Person.prototype) // true
// eslint-disable-next-line no-proto, no-restricted-properties
console.log(person1.__proto__.constructor === Person) // true
// eslint-disable-next-line no-proto, no-restricted-properties
console.log(person1.__proto__ === person2.__proto__) // true
// eslint-disable-next-line no-prototype-builtins
console.log(Person.prototype.isPrototypeOf(person1)) // true
// eslint-disable-next-line no-prototype-builtins
console.log(Person.prototype.isPrototypeOf(person2)) // true
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(person1) === Person.prototype) // true
console.log(person1 instanceof Person) // true
console.log(person1 instanceof Object) // true
console.log(Person.prototype instanceof Object) // true
下面五种操作 (方法/属性/运算符) 可以触发 JS 引擎读取一个对象的原型,
可以触发 getPrototypeOf() 代理方法的运行:
const obj = {}
const p = new Proxy(obj, {
getPrototypeOf(target) {
return Array.prototype
},
})
console.log(
Object.getPrototypeOf(p) === Array.prototype, // true
Reflect.getPrototypeOf(p) === Array.prototype, // true
// eslint-disable-next-line no-prototype-builtins
Array.prototype.isPrototypeOf(p), // true
// eslint-disable-next-line no-proto, no-restricted-properties
p.__proto__ === Array.prototype, // true
// eslint-disable-next-line unicorn/no-instanceof-array
p instanceof Array // true
)
Set the inherited property will create own property (overrides value of inherited property):
const proto = {
protoProp: 'a',
}
const obj = {
__proto__: proto,
objProp: 'b',
}
// In the beginning, obj has one own property:
assert.deepEqual(Object.keys(obj), ['objProp'])
obj.protoProp = 'x'
// Created a new own property:
assert.deepEqual(Object.keys(obj), ['objProp', 'protoProp'])
// The inherited property itself is unchanged:
assert.equal(proto.protoProp, 'a')
// The own property overrides the inherited property:
assert.equal(obj.protoProp, 'x')
Object Conversion
对象转换为布尔值:
- 直接转换为 true (包装类型也一样), 不调用 valueOf 和 toString.
对象转换为数字:
- 如果对象具有 valueOf 方法 (返回原始值), 则将该原始值转换为数字 (转换失败会返回 NaN), 并返回这个数字.
- 如果对象具有 toString 方法 (返回原始值), 则将该原始值转换为数字 (转换失败会返回 NaN), 并返回这个数字.
- 转换失败, 抛出
TypeError.
对象转换为字符串:
- 如果对象具有 toString 方法 (返回原始值), 则将该原始值转换为字符串, 并返回该字符串.
- 如果对象具有 valueOf 方法 (返回原始值), 则将该原始值转换为字符串, 并返回该字符串.
- 转换失败, 抛出
TypeError.
x | Object(x) |
|---|---|
undefined | {} |
null | {} |
boolean | new Boolean(x) |
number | new Number(x) |
bigint | An instance of BigInt (new throws TypeError) |
string | new String(x) |
symbol | An instance of Symbol (new throws TypeError) |
object | x |
// 保存原始的valueOf
const valueOf = Object.prototype.valueOf
const toString = Object.prototype.toString
// 添加valueOf日志
// eslint-disable-next-line no-extend-native
Object.prototype.valueOf = function () {
console.log('valueOf')
return valueOf.call(this)
}
// 添加toString日志
// eslint-disable-next-line no-extend-native
Object.prototype.toString = function () {
console.log('toString')
return toString.call(this)
}
const a = {}
// eslint-disable-next-line no-new-wrappers, unicorn/new-for-builtins
const b = new Boolean(false)
if (a)
console.log(1)
if (b)
console.log(2)
// output:
// 1
// 2
// 未调用valueOf和toString, 符合 [对象到布尔值] 的转换规则
// 保存原始的valueOf
const valueOf = Object.prototype.valueOf
const toString = Object.prototype.toString
// 添加valueOf日志
// eslint-disable-next-line no-extend-native
Object.prototype.valueOf = function () {
console.log('valueOf')
return valueOf.call(this)
}
// 添加toString日志
// eslint-disable-next-line no-extend-native
Object.prototype.toString = function () {
console.log('toString')
return toString.call(this)
}
let a = {}
console.log(++a)
// output:
// valueOf
// toString
// NaN
// 1. valueOf方法返回的是对象本身, 不是原始值, 继续执行
// 2. toString方法返回的是”[object Object]”, 是原始值(字符串), 将字符串转换为数字NaN
// 保存原始的valueOf
const valueOf = Object.prototype.valueOf
const toString = Object.prototype.toString
// 添加valueOf日志
// eslint-disable-next-line no-extend-native
Object.prototype.valueOf = function () {
console.log('valueOf')
return '1' // 强制返回原始值
}
// 添加toString日志
// eslint-disable-next-line no-extend-native
Object.prototype.toString = function () {
console.log('toString')
return toString.call(this)
}
let a = {}
console.log(++a)
// output:
// valueOf
// 2
// valueOf 返回原始值(字符串), 直接将该字符串转换为数字, 得到 1
// 保存原始的valueOf
const valueOf = Object.prototype.valueOf
const toString = Object.prototype.toString
// 添加valueOf日志
// eslint-disable-next-line no-extend-native
Object.prototype.valueOf = function () {
console.log('valueOf')
return valueOf.call(this)
}
// 添加toString日志
// eslint-disable-next-line no-extend-native
Object.prototype.toString = function () {
console.log('toString')
return toString.call(this)
}
const a = {}
alert(a)
// output:
// toString
// 弹出 "[object Object]"
// 调用toString方法, 返回了字符串”[object Object]”, 对象最终转换为该字符串
// 保存原始的valueOf
const valueOf = Object.prototype.valueOf
const toString = Object.prototype.toString
// 添加valueOf日志
// eslint-disable-next-line no-extend-native
Object.prototype.valueOf = function () {
console.log('valueOf')
return valueOf.call(this)
}
// 添加toString日志
// eslint-disable-next-line no-extend-native
Object.prototype.toString = function () {
console.log('toString')
return this
}
const a = {}
alert(a)
// output:
// toString
// valueOf
// Uncaught TypeError: Cannot convert object to primitive value
// 调用toString方法, 返回的不是 primitive value, 继续执行
// 调用valueOf方法, 返回的不是 primitive value, 继续执行
// 抛出 TypeError
Object Constructor
- 首字母大写.
- 所有函数 (包括构造函数) 有
prototype属性.
Object Literal Creation
对象字面量由 Object 构造函数隐式构造;
const obj = {
name: 'sabertazimi',
}
console.log(obj[[proto]] === Object.prototype) // true
Object New Constructor
new 构造函数作用原理如下:
- 形成原型链: 隐式原型指向构造函数的原型对象
obj.__proto__ = constructor.prototype - 构造函数对象 (Constructor) 与原型对象 (Prototype) 之间形成闭环:
Constructor.prototype = Prototype.Prototype.constructor = Constructor.
function newInstance(constructor, ...args) {
// var this = Object.create(Person.prototype);
// this.__proto__ = F.prototype
// F.prototype = Person.prototype
// 即 this.__proto__ = Person.prototype;
const obj = {}
obj[[proto]] = constructor.prototype
constructor.apply(obj, args)
return obj
}
// =>
const instance = new Constructor(arguments)
function Employee(name) {
this.name = name
this.getName = function () {
return this.name
}
}
const employee = newInstance(Employee, 'Jack')
// =>
const employee = new Employee('Jack')
new.target:
function Foo() {
if (!new.target)
throw new Error('Foo() must be called with new')
}
function Waffle() {
// 当未使用 `new` 关键字时, `this` 指向全局对象
if (!(this instanceof Waffle))
return new Waffle()
// 正常构造函数
this.tastes = 'yummy'
}
Object Create Constructor
- 原型式继承非常适合不需要单独创建构造函数, 但仍然需要在对象间共享信息的场合.
- 属性中包含的引用值始终会在相关对象间共享.
Object.create = function (o) {
if (arguments.length > 1) {
throw new Error(
'Object.create implementation only accepts the first parameter.'
)
}
function F() {}
F.prototype = o
return new F()
}
// 1. `F.prototype === o`.
// 2. `new F()` lead to `f.__proto__ === F.prototype`.
// Finally: `f.__proto__ === o`.
Constructor Return Value
- 返回
this或 user-defined literal object. - 当返回值为基本类型时, 仍然可得到
this指针指向的原有对象.
const ObjectMaker = function () {
this.name = 'This is it'
// user-defined literal object
// 直接忽略 this.name.
const that = {}
that.name = 'And that\'s that'
return that
}
const MyClass = function () {
this.name = 'sven'
return 'anne' // 返回 string.
}
const obj = new MyClass()
console.log(obj.name) // 输出: sven .
Constructor Instance Detection
若在实例对象的原型链 (__proto__) 中能找到构造函数的 prototype 属性 (Prototype 对象),
则返回true, 否则返回false:
// true only if
// 1. Foo.__proto__ === Bar.prototype
// 2. Foo.__proto__......__proto__ === Bar.prototype
console.log(Foo instanceof Bar)
Object Property Descriptor
Property Descriptor Definition
对象的属性描述符:
Object.defineProperty(O, Prop, descriptor).Object.defineProperties(O, descriptors).
数据描述符:
value: 属性值, 默认undefined.writable: 是否是只读 property, 默认false.enumerable: 是否可以被枚举 (for in), 默认false.configurable: 是否可以被删除与修改 descriptor, 默认false.
存取描述符:
get: 返回 property 值的方法, 默认undefined.set: 为 property 设置值的方法, 默认undefined.enumerable: 是否可以被枚举 (for in), 默认false.configurable: 是否可以被删除与修改 descriptor, 默认false.
interface DataPropertyDescriptor {
value?: any
writable?: boolean
enumerable?: boolean
configurable?: boolean
}
interface AccessorPropertyDescriptor {
get?: (this: any) => any
set?: (this: any, v: any) => void
enumerable?: boolean
configurable?: boolean
}
type PropertyDescriptor = DataPropertyDescriptor | AccessorPropertyDescriptor
Object.defineProperty(o, 'age', {
value: 24,
writable: true,
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
})
Object.defineProperty(o, 'sex', {
value: 'male',
writable: false, // 不可赋值
enumerable: false, // 不可遍历/枚举
configurable: false,
})
Object.defineProperties(o, {
age: {
value: 24,
writable: true,
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
},
sex: {
value: 'male',
writable: false,
enumerable: false,
configurable: false,
},
})
Object.defineProperties(o, {
kind: {
value: 'Plate 1x3',
writable: true,
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
},
color: {
value: 'yellow',
writable: true,
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
},
description: {
get() {
return `${this.kind} (${this.color})`
},
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
},
})
Object keys (excluding Symbols) are strings under the hood, object keys are automatically converted into strings:
const obj = { 1: 'a', 2: 'b', 3: 'c' }
const set = new Set([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
Object.hasOwn(obj, '1') // true
Object.hasOwn(obj, 1) // true
set.has('1') // false
set.has(1) // true
const a = {}
const b = { key: 'b' }
const c = { key: 'c' }
a[b] = 123
a[c] = 456
console.log(a[b]) // a["[object Object]"] = 456
Object keys 遍历顺序:
- 首先遍历所有数值键, 按照数值升序排列.
- 其次遍历所有字符串键, 按照加入时间升序排列.
- 最后遍历所有
Symbol键, 按照加入时间升序排列.
Property Descriptor Functions
Object.create(prototype[, descriptors]).
const o = Object.create({
say() {
alert(this.name)
},
name: 'Byron',
})
const obj = Object.create(Object.prototype, {
kind: {
value: 'Plate 1x3',
writable: true,
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
},
color: {
value: 'yellow',
writable: true,
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
},
description: {
get() {
return `${this.kind} (${this.color})`
},
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
},
})
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(object, property).Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(object).
Object.defineProperties(target, Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(source))
const clone = Object.create(
Object.getPrototypeOf(obj),
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(obj)
)
Object.hasOwn(object, property): Boolean.inoperator: 检测实例及其原型链上所有属性名.
// Arrays
const trees = ['redwood', 'bay', 'cedar', 'oak', 'maple']
const truthy = 0 in trees
const truthy = 3 in trees
const falsy = 6 in trees
const falsy = 'bay' in trees
const truthy = 'length' in trees
const truthy = Symbol.iterator in trees
// Predefined objects
const truthy = 'PI' in Math
// Custom objects
const car = { make: 'Honda', model: 'Accord', year: 1998 }
const truthy = 'make' in car
const truthy = 'model' in car
for...in: 获取实例及其原型链上所有可枚举属性名.Object.getOwnPropertySymbols(object): 获取实例上 Symbol 属性名.Object.getOwnPropertyNames(object): 获取实例上非 Symbol 属性名 (包括不可枚举属性名).Object.keys(object): 获取实例上可枚举属性名.
const k1 = Symbol('k1')
const k2 = Symbol('k2')
const o = {
1: 1,
first: 'first',
[k1]: 'sym2',
second: 'second',
0: 0,
}
o[k2] = 'sym2'
o[3] = 3
o.third = 'third'
o[2] = 2
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyNames(o))
// ['0', '1', '2', '3', 'first', 'second', 'third']
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertySymbols(o))
// [Symbol(k1), Symbol(k2)]
function Person() {}
Person.prototype.name = 'Nicholas'
Person.prototype.age = 29
Person.prototype.job = 'Software Engineer'
Person.prototype.sayName = function () {
console.log(this.name)
}
const keys = Object.keys(Person.prototype)
console.log(keys) // 'name, age, job, sayName'
const p1 = new Person()
p1.name = 'Rob'
p1.age = 31
const p1keys = Object.keys(p1)
console.log(p1keys) // '[name, age]'
Object.values(O): object own enumerable property values.Object.entries(O): object own enumerable string-keyed property[key, value]pairs.Object.fromEntries().
const score = {
saber: 42,
todd: 19,
ken: 4,
gan: 41,
}
Object.keys(score).map(k => score[k])
// => [ 42, 19, 4, 41 ]
Object.values(score)
// => [ 42, 19, 4, 41 ]
Object.entries(score)
/**
* =>
* [
* [ 'saber', 42 ],
* [ 'todd', 19 ],
* [ 'ken', 4 ],
* [ 'gan', 41 ],
* ]
*/
function findKey(object, callback, thisValue) {
for (const [key, value] of Object.entries(object)) {
if (callback.call(thisValue, value, key, object))
return key
}
return undefined
}
const object = { x: 42, y: 50, abc: 9001 }
const result = Object.fromEntries(
Object.entries(object)
.filter(([key, value]) => key.length === 1)
.map(([key, value]) => [key, value * 2])
)
const map = new Map(Object.entries(object))
const objectCopy = Object.fromEntries(map)
function pick(object, ...keys) {
const filteredEntries = Object.entries(object).filter(([key, _value]) =>
keys.includes(key)
)
return Object.fromEntries(filteredEntries)
}
function invert(object) {
const mappedEntries = Object.entries(object).map(([key, value]) => [
value,
key,
])
return Object.fromEntries(mappedEntries)
}
function mapObject(object, callback, thisValue) {
const mappedEntries = Object.entries(object).map(([key, value]) => {
const mappedValue = callback.call(thisValue, value, key, object)
return [key, mappedValue]
})
return Object.fromEntries(mappedEntries)
}
| Operation (Only Enumerable) | String Key | Symbol Key | Inherited |
|---|---|---|---|
Object.keys() | ✔ | ✘ | ✘ |
Object.values() | ✔ | ✘ | ✘ |
Object.entries() | ✔ | ✘ | ✘ |
Object.assign() | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ |
Spreading {...x} | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ |
JSON.stringify() | ✔ | ✘ | ✘ |
for...in | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ |
| Operation (Include Non-enumerable) | String Key | Symbol Key | Inherited |
|---|---|---|---|
Object.getOwnPropertyNames() | ✔ | ✘ | ✘ |
Object.getOwnPropertySymbols() | ✘ | ✔ | ✘ |
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors() | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ |
Reflect.ownKeys() | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ |
Object.preventExtensions(O)/Object.isExtensible(O): 不可新增属性, 可删除/修改属性.Object.seal(O)/Object.isSealed(O): 设置configurable为 false (不可删除, 不可修改 descriptor), 可修改属性.Object.freeze(O)/Object.isFrozen(O): 不可新增/删除/修改属性 (Shallow).
const obj = Object.freeze({ foo: {} })
obj.bar = 123
// TypeError: Can't add property bar, object is not extensible
obj.foo = {}
// TypeError: Cannot assign to read only property 'foo' of #<Object>
obj.foo.qux = 'abc'
console.log(obj.foo.qux)
// 'abc'
Private Property and Method
Private Property
实现方式: 闭包
function Gadget() {
// private member
const name = 'iPod'
// public function
this.getName = function () {
return name
}
}
Private Method
getter: 返回基本类型值/引用类型深拷贝(POLA 最低授权原则).
function Gadget() {
// private member
const pref = {}
// public function
this.getPref = function () {
return pref.clone()
}
}
即使函数模式 + 揭示模式:
- 实现私有属性与私有方法.
- 提供私有方法的公共(读/执行 not 写)接口,公共接口发生意外,私有方法仍安全.
// 匿名即时函数模式.
const obj = (function () {
// private member
const name = 'tazimi'
// private method
const getName = function getName() {
return name
}
// 闭包
return {
// 公共接口 - 私有方法
getName,
}
})()
Static Property and Method
Static Property
实现方式: 闭包/原型代理
Static Method
直接向构造函数添加方法
Object.isArray = function () {}
Object Property
编写函数时,一般用[]访问对象属性
Object Method
为 prototype 添加方法,可以通过实现语法糖 method()简化代码(链模式)
if (typeof Function.prototype.method !== 'function') {
// eslint-disable-next-line no-extend-native
Function.prototype.method = function (name, implementation) {
this.prototype[name] = implementation
return this
}
}
const Person = function (name) {
this.name = name
}
.method('getName', function () {
return this.name
})
.method('setName', function (name) {
this.name = name
return this
})
Object Clone
Object Shallow Clone
Object.assign:
- Enumerable: 可枚举属性扩展.
- Own: 自有属性扩展.
- Shallow: 浅拷贝扩展.
- Trigger
sourceObj.setand changesourceObj.
const dest = {}
const src = { a: {} }
Object.assign(dest, src)
// 浅复制意味着只会复制对象的引用
console.log(dest) // { a :{} }
console.log(dest.a === src.a) // true
... object spread syntax:
- Enumerable: 可枚举属性扩展.
- Own: 自有属性扩展.
- Shallow: 浅拷贝扩展.
- Not copy prototype (
__proto__). - Not copy getter and setter.
- Not trigger
sourceObj.setand not changesourceObj(create new properties).
// Shallow copy
const foo = { a: 1 }
const bar = { b: 2, c: { d: 3 } }
const foobar = { ...foo, ...bar }
console.log(foobar.c === bar.c) // true
// Not copy prototype (`__proto__`)
class MyClass {}
const original = new MyClass()
assert.equal(original instanceof MyClass, true)
const copy = { ...original }
assert.equal(copy instanceof MyClass, false)
Object Deep Clone
Recursively copy all properties of an object:
function deepClone(original) {
if (Array.isArray(original)) {
return original.map(elem => deepClone(elem))
} else if (typeof original === 'object' && original !== null) {
return Object.fromEntries(
Object.entries(original).map(([key, value]) => [key, deepClone(value)])
)
} else {
// Primitive value: atomic, no need to copy
return original
}
}
function deepUpdate(original, keys, value) {
if (keys.length === 0)
return value
const currentKey = keys[0]
if (Array.isArray(original)) {
return original.map((v, index) =>
index === currentKey ? deepUpdate(v, keys.slice(1), value) : v
)
} else if (typeof original === 'object' && original !== null) {
return Object.fromEntries(
Object.entries(original).map(([k, v]) =>
k === currentKey ? [k, deepUpdate(v, keys.slice(1), value)] : [k, v]
)
)
} else {
// Primitive value
return original
}
}
Using JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj)):
- Not copy prototype (
__proto__). - Not copy getter and setter.
- Not copy non-enumerable properties.
- Not copy Symbol properties.
- Not copy circular references.
- Not copy
undefined,function,symbol.
const obj = { a: 1, b: { c: 2 } }
const clone = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj))
console.log(clone) // { a: 1, b: { c: 2 } }
Using window.structuredClone():
// Create an object with a value and a circular reference to itself.
const original = { name: 'MDN' }
original.itself = original
// Clone it
const clone = structuredClone(original)
console.assert(clone !== original) // the objects are not the same (not same identity)
console.assert(clone.name === 'MDN') // they do have the same values
console.assert(clone.itself === clone) // and the circular reference is preserved
const room1 = {
people: ['Alan', 'Bob'],
}
const room2 = structuredClone(room1)
room2.people.push('Charlie')
room1.people.pop()
console.log(room2.people) // ["Alan", "Bob", "Charlie"]
console.log(room1.people) // ["Alan"]
Object Inheritance
Prototype Proxy Inheritance
可用于所有继承模式中, 减少内存消耗:
const inherit = (function () {
// 减少继承过程中父类的实例化,减少资源消耗
// 实例化一个空类所需资源更少
const F = function () {}
return function (C, P) {
// c.__proto__ = C.prototype = f
// f.__proto__ = F.prototype
// F.prototype = P.prototype
// c.__proto__.__proto__ = f.__proto__ = P.prototype
F.prototype = P.prototype // f.__proto__ = F.prototype = P.prototype
C.prototype = new F() // C.prototype = f
C.prototype.constructor = C
C.super = P.prototype // 此句可提高代码的重用性
}
})()
Child.prototype.add = function () {
return Child.super.add.call(this)
}
Class Simulation Inheritance
复制式地继承, 将会消耗大量内存单元:
const classSim = function (Parent, props) {
// 新的构造函数
const Child = function (...args) {
if (
Child.uber
&& Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(Child.uber, '_construct')
) {
Child.uber._construct.apply(this, args)
}
if (Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(Child.prototype, '_construct'))
Child.prototype._construct.apply(this, args)
}
// 类式继承
Parent = Parent || Object
// 代理构造函数F
const F = function () {}
F.prototype = Parent.prototype
Child.prototype = new F()
Child.prototype.constructor = Child
// 添加属性与方法
for (const i in props) {
if (Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(props, i))
Child.prototype[i] = props[i]
}
// return the "class"
return Child
}
const SuperMan = classSim(Man, {
_construct(what) {
console.log('SuperMan\'s constructor')
},
getName() {
const name = SuperMan.uber.getName.call(this)
return `I am ${name}`
},
})
Composite Inheritance
原型继承 (设置原型) 与类式继承 (借用构造函数) 组合继承模式:
child.prototype = new Parent(); Child.prototype.constructor = Child.Parent.apply(this, arguments): 借用构造函数可以防止引用类型被迫共享.- 此模式会调用两次父类构造函数, 使得子类属性继承两次, 存在一定的效率问题.
function Parent(name) {
this.name = name || 'Adam'
}
// Adding functionality to the prototype
Parent.prototype.say = function () {
return this.name
}
// Child constructor
function Child(...args) {
// 解决引用类型共享问题
Parent.apply(this, args)
this.childName = 'Child Name'
}
// Child.prototype = Object.create(Parent.prototype);
Child.prototype = new Parent() // 设置原型链,建立继承关系
Child.prototype.constructor = Child // 使得 Prototype 对象与 Constructor 对象形成闭环
Class
Class Prototype
Class定义不能提升.Class具有块作用域.Class内部为严格模式.Class内部定义方法不可枚举.Class所有方法 (包括静态方法和实例方法) 都没有原型对象.prototype, 没有[[construct]], 不能使用new调用.Class必须使用new调用, 否则会报错.typeof Class:function.
class A {
constructor(value) {
this.val = value
}
}
class B extends A {
constructor(value) {
super(value)
console.log('New')
}
}
const b = new B(6)
console.log(B[[proto]] === A) // true
console.log(B.prototype.constructor === B) // true
console.log(B.prototype[[proto]] === A.prototype) // true
console.log(b[[proto]] === B.prototype) // true
function AA(value) {
this.val = value
}
function BB(value) {
AA.call(this, value)
}
BB.prototype = Object.create(AA.prototype)
BB.prototype.constructor = BB
const bb = new BB(6)
console.log(BB[[proto]] === Function.prototype) // true (not consistence to Class)
console.log(BB.prototype.constructor === BB) // true
console.log(BB.prototype[[proto]] === AA.prototype) // true
console.log(bb[[proto]] === BB.prototype) // true
| Writable | Enumerable | Configurable | |
|---|---|---|---|
Foo.prototype | false | false | false |
Foo.prototype.constructor | false | false | true |
Static properties Foo.* | true | false | true |
Prototype properties Foo.prototype.* | true | false | true |
Class Inheritance
- 隔离: 添加到
this的所有属性都会存在于不同的实例上. - 共享:
- 在类块中定义的所有方法都会定义在类的原型上.
- 静态属性定义在类本身上.
class Person {
constructor() {
// 添加到 this 的所有内容都会存在于不同的实例上
this.locate = () => console.log('instance', this)
}
// 在类块中定义的所有内容都会定义在类的原型上
locate() {
console.log('prototype', this)
}
// 定义在类本身上
static locate() {
console.log('class', this)
}
}
const p = new Person()
p.locate() // instance, Person {}
Person.prototype.locate() // prototype, {constructor: ... }
Person.locate() // class, class Person {}
Class Definition | Class Prototype | Class.prototype Prototype |
|---|---|---|
C | Function.prototype | Object.prototype |
C extends null | Function.prototype | null |
C extends Object | Object | Object.prototype |
C extends B | B | B.prototype |
- ES5 继承先创造子类实例对象
this, 然后再将父类的属性与方法添加到this上 (Parent.apply(this)), 实例在前继承在后. - ES6 继承先将父类的属性与方法添加到
this上 (必须先调用super()方法), 然后再用子类的构造函数修改this, 继承在前实例在后. - ES5 继承
Child.__proto__ === Function.prototype. - ES6 继承
Child.__proto__ === Parent, 子类可以直接通过[[proto]]寻址到父类.
Super Class
super:
super只能在派生类构造函数和静态方法中使用.- 不能单独引用
super关键字, 要么用它调用构造函数, 要么用它引用静态方法. - 调用
super()会调用父类构造函数, 并将返回的实例赋值给this. - 在类构造函数中, 不能在调用
super()之前引用this. super()等价于调用构造函数, 若需给父类构造函数传参, 则需手动传入.- 若没有显式定义派生类构造函数, 在实例化派生类时会自动调用
super(), 且会自动传入所有传给派生类的参数. - 若显式定义了派生类构造函数, 则必须在其中调用
super(), 或返回一个对象. - 实例化时检测
new.target是不是抽象基类, 可以阻止对抽象基类的实例化.
Abstract Base Class
class Shape {
constructor() {
if (new.target === Shape)
throw new TypeError('This class cannot be instantiated directly.')
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {
constructor(length, width) {
super()
this.length = length
this.width = width
}
}
const x = new Shape() // throws error
const y = new Rectangle(3, 4) // no error
console.log(y instanceof Shape) // true
Class Expression
// Anonymous class expression
const Person = class {}
// Named class expression
const Person = class PersonName {
identify() {
console.log(Person.name, PersonName.name)
}
}
const p = new Person()
p.identify() // PersonName PersonName
console.log(Person.name) // PersonName
console.log(PersonName) // ReferenceError: PersonName is not defined
Class Constructor
class A {
constructor() {
console.log(new.target.name)
}
}
class B extends A {
constructor() {
super()
console.log('New')
}
}
const a = new A() // logs "A"
const b = new B() // logs "B"
class C {
constructor() {
console.log(new.target)
}
}
class D extends C {
constructor() {
super()
console.log('New')
}
}
const c = new C() // logs class C{constructor(){console.log(new.target);}}
const d = new D() // logs class D extends C{constructor(){super();}}
Class Private Member
- Private access.
- Aren't stored in
.prototype. - Aren't create instance own properties.
class Dong {
constructor() {
this.#name = 'dog'
this.#age = 20
this.friend = 'cat'
}
hello() {
return `I'm ${this.#name} ${this.#age} years old`
}
}
Private member can only be accessed inside body of its class, can’t even access it from a subclass:
class SuperClass {
#superProp = 'superProp'
}
class SubClass extends SuperClass {
getSuperProp() {
return this.#superProp
}
}
// SyntaxError: Private field '#superProp'
// must be declared in an enclosing class
class Color {
#name
constructor(name) {
this.#name = name
}
static getName(obj) {
return obj.#name
}
}
class Person {
#name
constructor(name) {
this.#name = name
}
}
// Can’t access the private slot #name of a Person:
assert.equal(Color.getName(new Color('green')), 'green')
assert.throws(() => Color.getName(new Person('Jane')), {
name: 'TypeError',
message:
'Cannot read private member #name from'
+ ' an object whose class did not declare it',
})
Private member never clash,
they aren't stored in .prototype objects and aren't inherited:
class SuperClass {
#privateField = 'super'
getSuperPrivateField() {
return this.#privateField
}
}
class SubClass extends SuperClass {
#privateField = 'sub'
getSubPrivateField() {
return this.#privateField
}
}
const inst = new SubClass()
assert.equal(inst.getSuperPrivateField(), 'super')
assert.equal(inst.getSubPrivateField(), 'sub')
Private member can't be accessed by Reflect.ownKeys():
class InstPrivateClass {
#privateField1 = 'private field 1'
#privateField2
constructor(value) {
this.#privateField2 = value
}
}
// No instance properties were created
const inst = new InstPrivateClass('constructor argument')
assert.deepEqual(Reflect.ownKeys(inst), [])
Private member WeakMap polyfill:
function classPrivateFieldGet(receiver, state) {
return state.get(receiver)
}
function classPrivateFieldSet(receiver, state, value) {
state.set(receiver, value)
}
const dongName = new WeakMap()
const dongAge = new WeakMap()
class Dong {
constructor() {
classPrivateFieldSet(this, dongName, 'dong')
classPrivateFieldSet(this, dongAge, 20)
}
hello() {
return `I'm ${classPrivateFieldGet(this, dongName)}, ${classPrivateFieldGet(
this,
dongAge
)} years old`
}
}
Class Public Fields
class SuperClass {
superProp = console.log('superProp')
constructor() {
console.log('super-constructor')
}
}
class SubClass extends SuperClass {
subProp = console.log('subProp')
constructor() {
console.log('BEFORE super()')
super()
console.log('AFTER super()')
}
}
const sub = new SubClass()
// Output:
// 'BEFORE super()'
// 'superProp'
// 'super-constructor'
// 'subProp'
// 'AFTER super()'
Class Static Blocks
Static blocks have access to class private member. Its mainly useful whenever set up multiple static fields.
class Foo {
static #count = 0
get count() {
return Foo.#count
}
static {
try {
const lastInstances = loadLastInstances()
Foo.#count += lastInstances.length
} catch {}
}
}
class Translator {
static translations = {
yes: 'ja',
}
static englishWords = []
static germanWords = []
static {
for (const [english, german] of Object.entries(translations)) {
this.englishWords.push(english)
this.germanWords.push(german)
}
}
}
class SuperClass {
static superField1 = console.log('superField1')
static {
assert.equal(this, SuperClass)
console.log('static block 1 SuperClass')
}
static superField2 = console.log('superField2')
static {
console.log('static block 2 SuperClass')
}
}
class SubClass extends SuperClass {
static subField1 = console.log('subField1')
static {
assert.equal(this, SubClass)
console.log('static block 1 SubClass')
}
static subField2 = console.log('subField2')
static {
console.log('static block 2 SubClass')
}
}
// Output:
// 'superField1'
// 'static block 1 SuperClass'
// 'superField2'
// 'static block 2 SuperClass'
// 'subField1'
// 'static block 1 SubClass'
// 'subField2'
// 'static block 2 SubClass'
Class Best Practice
Avoid using class when:
- Singleton:
- Only instantiate your class once in a given runtime.
- Stateless:
- Data structure no need for local state.
- Data structure no need for extending.
- Redundant:
- Minimal public methods.
- Constructors are only used for dependency injection.
- Constructors are always called with same arguments.
- Want to avoid using
this.
Global Object
// 立即函数模式:
// 此时返回值不是函数本身, 而是函数执行后的 return 语句返回值.
const global = (function () {
// 返回全局对象
return this
})()
Global Object 属性:
- undefined.
- NaN.
- Infinity.
- Object.
- Array.
- Function.
- Boolean.
- String.
- Number.
- Date.
- RegExp.
- Symbol.
- Error.
- EvalError.
- RangeError.
- ReferenceError.
- SyntaxError.
- TypeError.
- URIError.
- encodeURI.
- encodeURIComponent.
- decodeURI.
- decodeURIComponent.
- eval.
;(function () {
// Grab browser's default global variables.
const iframe = window.document.createElement('iframe')
iframe.src = 'about:blank'
window.document.body.appendChild(iframe)
const browserGlobals = Object.keys(iframe.contentWindow)
window.document.body.removeChild(iframe)
// Get the global variables added at runtime by filtering out the browser's
// default global variables from the current window object.
const runtimeGlobals = Object.keys(window).filter((key) => {
const isFromBrowser = browserGlobals.includes(key)
return !isFromBrowser
})
console.log('Runtime globals', runtimeGlobals)
})()
Function
- 函数是对象.
- 函数提供局部作用域.
- Object 是 Function 的实例对象, Function.prototype是 Object 的实例对象.
const truthy = Object[[proto]] === Function.prototype // true
const truthy = Function[[proto]] === Function.prototype // true
const truthy = Function[[proto]][[proto]] === Object.prototype // true
Implicit Invocation
Function Invocation普通调用模式:this绑定至全局对象/undefined(strict mode)- setTimeout 和 setInterval 中传入的 Callbacks
会自动转变为
Function Invocation,thisbind to global/undefined object. - React Class Component 中传入的 Event Handlers
会自动转变为
Function Invocation, 需要显式地this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this);
- setTimeout 和 setInterval 中传入的 Callbacks
会自动转变为
Method Invocation方法调用模式:this绑定至此方法所属的对象.
// Non-strict mode:
window.identity = 'The Window'
const object = {
identity: 'My Object',
getIdentityFunc() {
return function () {
return this.identity
}
},
}
// Function invocation:
// Anonymous closure function `this` bind to `window`.
console.log(object.getIdentityFunc()()) // 'The Window'
add(1, 2) // `this` -> `global`
const obj = {
value: 1,
foo() {
// 若不将 `this` 赋值给 `that`, 而在内部函数中直接使用 `this.value`,
// 则会发生错误: 内部函数的 `this` 指向全局对象而不是 `obj`.
// eslint-disable-next-line ts/no-this-alias
const that = this
function inner() {
return that.value
}
return inner()
},
}
obj.foo() // 1
class Hero {
constructor(heroName) {
this.heroName = heroName
}
logName() {
console.log(this.heroName)
}
}
const batman = new Hero('Batman')
setTimeout(batman.logName, 1000)
// after 1 second logs "undefined"
Explicit Invocation
Apply/Bind/Call Invocation:
函数引用不可以改变函数定义作用域 (scope), 但可以改变函数执行作用域 (context).
this.construct = Foo
this.construct(options)
// =>
Foo.call(this, options)
Function.call(contextObj, arg1, arg2, ...)Function.apply(contextArray, [arg1, arg2, ...]/arguments)- call 效率高于 apply.
window.function.call()
window.function.apply()
// js解释器临时将数组/字符串包装成对象原型.
;[].arrayStaticFunction.call()
;[].arrayStaticFunction.apply()
Array.prototype.arrayStaticFunction.call()
Array.prototype.arrayStaticFunction.apply()
''.stringStaticFunction.call()
''.stringStaticFunction.apply()
String.prototype.stringStaticFunction.call()
String.prototype.stringStaticFunction.apply()
相当于:
context.function(arguments)
Explicit Bind Invocation
- Change function runtime context (ignore innovation pattern
function/method/new/call/apply). - Curry function.
- Can't change
thisin arrow function.
const boundFunc = func.bind(context, arg1, arg2, argN)
Explicit Call and Apply Invocation
function bind(o, m) {
return function (...args) {
return m.apply(o, args)
}
}
const one = {
name: 'object',
say(greet) {
return `${greet}, ${this.name}`
},
}
const two = { name: 'another object' }
const twoSay = bind(two, one.say)
twoSay('yo') // "yo, another object"
Constructor Invocation
Constructor invocation (new call):
this绑定至传入的空对象.new.target引用构造函数.
function newConstructor(Func, ...args) {
// 1. 创建一个新对象
const obj = {}
// 2. 新对象原型指向构造函数原型对象
obj[[proto]] = Func.prototype
// 3. 将构建函数的 `this` 指向新对象
const result = Func.apply(obj, args)
// 4. 返回对象
return result instanceof Object ? result : obj
}
new constructor invocation >
explicit invocation >
implicit invocation >
default invocation.
Arrow Function Invocation
- No
thisbinding (lexical scope):thisdefined where arrow function defined (not called).- Not suited as method:
thisin arrow function bound to lexical scope, not bound to method receiver. apply/call/bindcan't changethisin arrow function.
- No
argumentsbinding (lexical scope). - Not suited as
newconstructor:- No
superbinding (lexical scope). - No
new.targetbinding (lexical scope).
- No
- No
function.prototype: arrow functionprototypeproperty isundefined. - No
yieldbinding: 箭头函数不能用作 Generator 函数.
const obj = {
foo() {
const inner = () => {
return this.value
}
return inner()
},
}
const func = obj.foo
obj.foo() // `this` in `inner` function refer to `obj`
func() // `this` in `inner` function refer to `window`
This Binding Invocation
function Call | Method Call | new Call | |
|---|---|---|---|
Traditional function (sloppy) | window | receiver | instance |
Traditional function (strict) | undefined | receiver | instance |
| Method (sloppy) | window | receiver | TypeError |
| Method (strict) | undefined | receiver | TypeError |
Generator function (sloppy) | window | receiver | TypeError |
Generator function (strict) | undefined | receiver | TypeError |
| Generator method (sloppy) | window | receiver | TypeError |
| Generator method (strict) | undefined | receiver | TypeError |
Arrow function | lexical | lexical | TypeError |
| Class | TypeError | TypeError | SC protocol |
Context and Scope
- 每个上下文都有一个关联的变量对象 (Variable Object), 这个上下文中定义的所有变量和函数都��存在于这个对象上.
- 每个执行环境拥有独立的作用域链, 例如独立活动对象 -> 独立全局对象:
scope chain->(list) [0]活动对象->[1]全局对象.- ES6 Block Scope -> Function Scope -> Global Scope.
- 全局上下文中关联的变量对象 (Variable Object), 会在代码执行期间始终存在.
- 函数上下文将其活动对象 (Activation Object) 用作变量对象 (Variable Object):
- 函数每次运行时, 都会新建执行环境上下文与作用域链, 执行完后销毁上下文与作用域链.
- 存在闭包时, 函数上下文关联的作用域链中被引用的活动对象不会被销毁.
- 可动态改变作用域链的语句:
with.try catch: 异常对象入列, 位于作用域链链首.
function createComparisonFunction(propertyName) {
return function (object1, object2) {
const value1 = object1[propertyName]
const value2 = object2[propertyName]
if (value1 < value2)
return -1
else if (value1 > value2)
return 1
else
return 0
}
}
const compare = createComparisonFunction('name')
const result = compare({ name: 'Nicholas' }, { name: 'Matt' })
执行上述代码后的上下文栈与作用域链如下图所示:
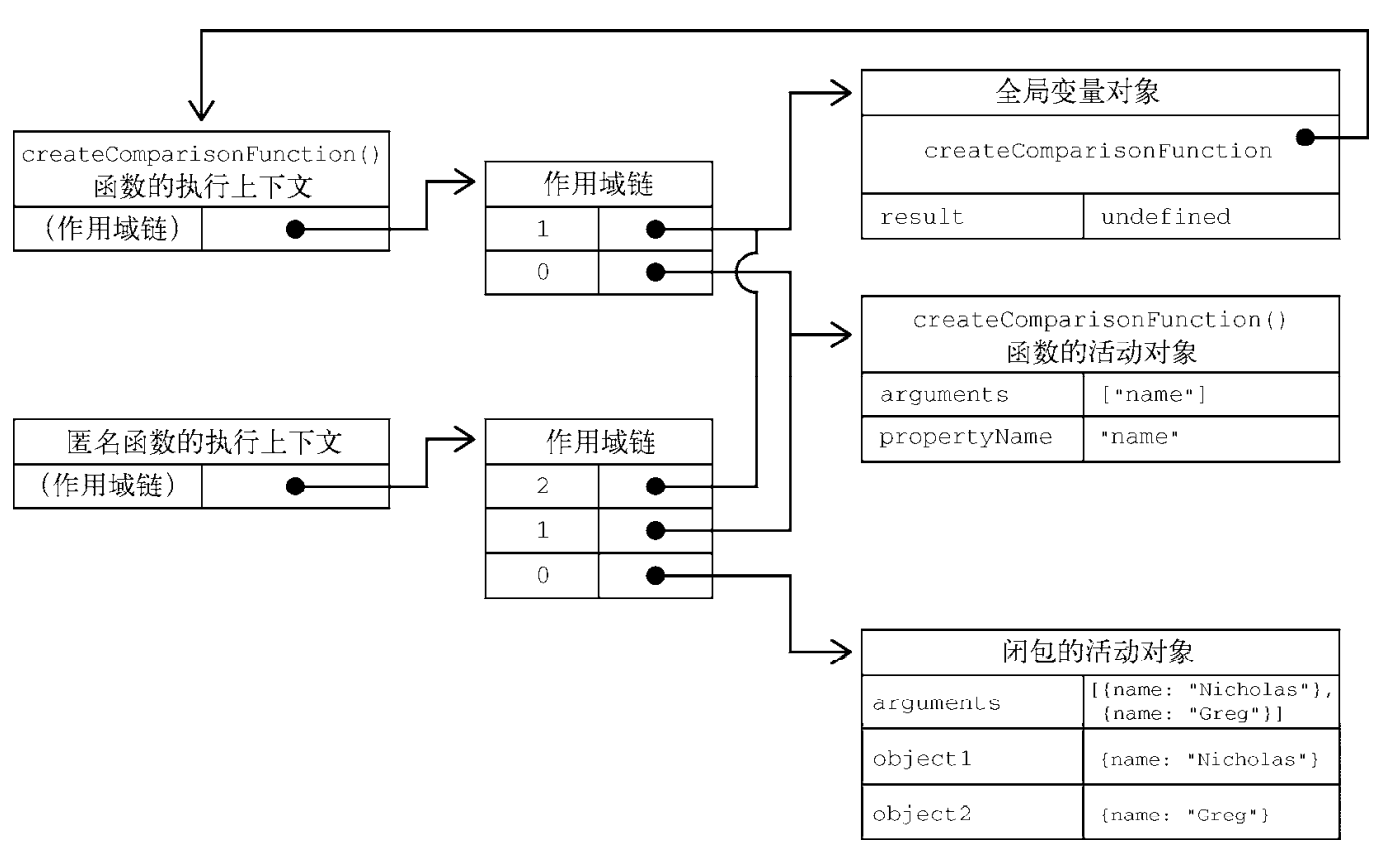
createComparisonFunction() 的活动对象并不能在它执行完毕后销毁,
因为匿名函数的作用域链中仍然存在对它的引用.
在 createComparisonFunction() 执行完毕后,
其执行上下文的作用域链会销毁,
但它的活动对象仍然会保留在内存中,
直到匿名函数被销毁后才会被销毁.
Function Name
- 所有函数对象都会暴露一个只读的
name属性, 其中包含关于函数的信息. - The spec operation
SetFunctionName(F, name, [, prefix])sets up functionname:- Getters and setters get prefixes
getandset. Function.prototype.bind()get prefixbound.- Function declaration name are set up when entering a scope (hoisted).
- Named function expression name are set up via
SetFunctionName(). - Arrow function and anonymous function expression name aren't set up
(
SetFunctionName()is not invoked).
- Getters and setters get prefixes
function foo() {}
const bar = function () {}
function baz() {}
console.log(foo.name) // foo
console.log(bar.name) // bar
console.log(baz.name) // baz
console.log((() => {}).name) // (空字符串)
// eslint-disable-next-line no-new-func
console.log(new Function().name) // anonymous
console.log(foo.bind(null).name) // bound foo
const dog = {
years: 1,
get age() {
return this.years
},
set age(newAge) {
this.years = newAge
},
}
const propertyDescriptor = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(dog, 'age')
console.log(propertyDescriptor.get.name) // get age
console.log(propertyDescriptor.set.name) // set age
Function Prototype
- 实例化对象没有 prototype 属性.
- 每个函数都有
prototype属性. prototype属性指向函数的原型对象 (由 JS 引擎自动创建).- 每个函数的
__proto__都指向Function.prototype.
Function Arguments
- 函数的参数在内部表现为一个数组: 函数不关心参数个数与参数类型, 不存在验证命名参数的机制.
arguments不是真正的数组, 但有length属性 (实参个数).
Arguments Callee
- 引用 arguments 所属 function, 可以利用 callee 实现匿名递归函数.
arguments.callee.length: 即function.length, 形参个数.- 严格模式下禁止使用
arguments.callee.
try {
// eslint-disable-next-line no-caller
if (arguments.length !== arguments.callee.length)
throw new Error('传递的参数个数不匹配')
} catch (err) {
console.log(err)
return this
}
Function Parameters
- 所有函数参数都是按值传递 (复制原子值/引用值).
function.length: number of parameters before the first one with a default value.- 无副作用的函数: 注意是否需要拷贝传入对象, 使原有对象不受函数影响, 并返回新对象.
const obj = {
value: 2,
}
function setValueEffect(obj, val) {
obj.value = val
return obj
}
function setValuePure(obj, val) {
const instance = extend({}, obj, { value: val })
return instance
}
Default Parameter
默认参数:
- 默认参数可以使用原子值/对象值/函数返回值.
- 函数调用且未传参时, 默认参数才会进行求值.
- 默认参数按照从左往右的顺序进行求值.
// Mark required parameters via a function that throws an exception
function foo(required = throwException()) {}
Rest Parameter
- Rest parameter is array containing all remaining arguments.
- Rest parameter can only be last parameter.
// Enforcing a maximum parameters
function f(x, y, ...empty) {
if (empty.length > 0)
throw new Error('Redundant parameters!')
}
Function Declaration
- 函数声明提升: 函数声明会在代码执行之前获得定义.
console.log(foo.name)
// Function Declaration 函数声明:
function foo() {}
const obj = {
say: function say() {},
}
- 函数声明对于函数内部而言无法修改:
const b = 10
;(function b() {
b = 20
console.log(b)
})()
// print out function b { ... }
Function Expression
任何时候, 只要函数被当作值来使用, 它就是一个函数表达式:
// 函数表达式:
const foo = function foo() {}
// `function f() {}` 是命名函数表达式:
const factorial = function f(num) {
if (num <= 1)
return 1
else
return num * f(num - 1)
}
The name funcExpr only exists inside the function body:
const func = function funcExpr() {
return funcExpr
}
assert.equal(func(), func)
assert.throws(() => funcExpr(), ReferenceError)
Immediately Invoked Function Expression
IIFE Pattern
立即函数模式, 通过调用立即匿名函数, 返回一个对象, 暴露公共接口 (Exposed to Public):
- IIFE Syntax:
- 函数表达式.
- 末尾添加括号(传参), 使函数立即执行.
- 将整个函数置于括号内.
- 闭包: 定义私有变量与特权方法.
- 返回对象: 即使通过外部代码改变返回对象的接口, 也不会影响原接口.
;(function () {
console.log('watch out')
})()
IIFE Return Value
Left hand side 不被赋予 function 值, 而被赋予函数执行后的返回值: 此返回值可设为函数, 可产生闭包.
const getResult = (function () {
const res = 2 + 2
return function () {
return res
}
})()
IIFE Usage
- 使得匿名函数内部的代码能够立即执行.
- 不泄漏只使用一次的局部变量与方法.
- 创建命名空间, 防止变量命名冲突.
const obj = (function () {
// private member
let name = 'tazimi'
// private method
// excluded in return object
// privileged method
function getName() {
return name
}
function setName(n) {
if (typeof n === 'string')
name = n
return this
}
// public method
function logName() {
console.log(name)
}
// 闭包
// 公共接口: 特权/公共方法
return {
// 特权方法
getName,
setName,
// 公共方法
log: logName,
}
})()
const App = App || {}
App.utils = {}
;(function () {
let val = 5
this.getValue = function () {
return val
}
this.setValue = function (newVal) {
val = newVal
}
// also introduce a new sub-namespace
this.tools = {}
}).apply(App.utils)
// inject new behavior into the tools namespace
// which we defined via the utilities module
;(function () {
this.diagnose = function () {
return 'diagnosis'
}
}).apply(App.utils.tools)
Tail Call Optimization
- Tail call optimization only work in strict mode
due to
func.argumentsandfunc.caller(forbidden in strict mode):func.argumentsandfunc.callerwill reference outer function stack frame, so can't reduce outer function stack frame. - Tail call optimization reduce function stack frame.
// Following function is not tail recursive:
function factorial(x) {
if (x <= 0)
return 1
else
return x * factorial(x - 1) // (A): Not tail position.
}
function factorial(n) {
return facRec(n, 1)
}
// Following function is tail recursive:
function facRec(x, acc) {
if (x <= 1)
return acc
else
return facRec(x - 1, x * acc) // (A): Tail position.
}
Closure
Closure is a function that remembers the variables from the place where it is defined (lexical scope), regardless of where it is executed later:
- 函数外部不可对函数内部进行赋值或引用.
- 函数中的闭包函数可对函数进行赋值或引用 (函数对于闭包来说是外部, 即内部引用外部).
- 特权性质 (Private Getter): 从外部通过闭包方法访问内部 (函数作用域) 局部变量.
- Local Scope -> Outer Functions Scope -> Global Scope.
- 闭包中的变量全部保存在堆内存中, 防止函数结束后变量内存被自动回收.
// global scope
const e = 10
function sum(a) {
return function (b) {
return function (c) {
// outer functions scope
return function (d) {
// local scope
return a + b + c + d + e
}
}
}
}
console.log(sum(1)(2)(3)(4)) // log 20
// BAD
function MyObject(name, message) {
this.name = name.toString()
this.message = message.toString()
this.getName = function () {
return this.name
}
this.getMessage = function () {
return this.message
}
}
// GOOD: avoid unnecessary
function MyObject(name, message) {
this.name = name.toString()
this.message = message.toString()
}
MyObject.prototype.getName = function () {
return this.name
}
MyObject.prototype.getMessage = function () {
return this.message
}
Closure Structure
- 优先级: this > 局部变量 > 形参 > arguments > 函数名.
innerFunc()has access toouterVarfrom its lexical scope, even being executed outside of its lexical scope.
function outerFunc() {
const outerVar = 'I am outside!'
function innerFunc() {
console.log(outerVar) // => logs "I am outside!"
}
return innerFunc
}
const myInnerFunc = outerFunc()
myInnerFunc()
Closure Usage
- 闭包实现封装.
- 闭包�实现私有属性与方法.
- 闭包实现工厂方法.
- 闭包实现对象缓存.
const createLoginLayer = (function (creator) {
let singleton
return function () {
if (!singleton)
singleton = creator()
return singleton
}
})(loginCreator)
const { called } = new (class {
count = 0
called = () => {
this.count++
console.log(`Called : ${this.count}`)
}
})()
called() // Called : 1
called() // Called : 2
Callback Function
// check if callback is callable
if (typeof callback !== 'function')
callback = false
// now callback:
if (callback)
callback()
const findNodes = function (callback) {
let i = 100000
const nodes = []
let found
// check if callback is callable
if (typeof callback !== 'function')
callback = false
while (i) {
i -= 1
// now callback:
if (callback)
callback(found)
nodes.push(found)
}
return nodes
}
当回调函数为对象方法时 (特别时方法中使用 this 指针),
需同时传入对象参数,
并利用 apply/call 改变执行环境.
const findNodes = function (callbackObj, callback) {
if (typeof callback === 'function')
callback.call(callbackObj, found)
}
const findNodes = function (callbackObj, callback) {
if (typeof callback === 'string')
callback = callbackObj[callback]
if (typeof callback === 'function')
callback.call(callbackObj, found)
}
Lazy Function Definition
Lazy Function Definition (Self-Defining Function):
- 第一次执行时,进行初始化并重新定义函数变量.
- 第二次执行时,不再进行初始化(函数被重定义至真正函数).
- 第一次执行为 promise, 将重复使用的部分进行初始化, 之后的调用不再浪费新空间, 提升性能.
// definition
let foo = function () {
// initialize code;
const t = new Date()
foo = function () {
return t
}
// 使得第一次调用可以产生预期值,保证每次调用的行为保持一致
return foo()
}
// first run: same behavior as second run
console.log(foo()) // t
// second run
console.log(foo()) // t
let addEvent = function (el, type, handle) {
addEvent = el.addEventListener
? function (el, type, handle) {
el.addEventListener(type, handle, false)
}
: function (el, type, handle) {
el.attachEvent(`on${type}`, handle)
}
// 保持每次调用对外表现行为一致
addEvent(el, type, handle)
}
Polymorphism Function
const greet = function greet(options, ...rest) {
// 运用 if/switch 方法分情况调用函数, 实现多态方法.
if (typeof options === 'string' && typeof methods[options] === 'function') {
// 方法集中含有此方法:
return methods[options](...rest)
}
}
多态最根本的作用: 通过把过程化的条件分支语句转化为对象的多态性, 从而消除条件分支语句.
每个对象的职责, 成为该对象的属性与方法, 被安装在对象内部, 每个对象负责它们自己的行为. 这些对象可以根据同一个消息, 有条不紊地分别进行各自的工作.
Eval Function
- 不要使用
eval()函数 - 不要使用字符串作参数 new Function();(会调用
eval函数) - 不要使用字符串作
setTimeOut/setInterval的第一个参数(会调用eval函数)
// Anti-pattern:
const property = 'name'
// eslint-disable-next-line no-eval
alert(eval(`obj.${property}`))
// Preferred:
const property = 'name'
alert(obj[property])
// Anti-pattern:
// eslint-disable-next-line no-implied-eval
setTimeout('myFunc()', 1000)
// eslint-disable-next-line no-implied-eval
setTimeout('myFunc(1, 2, 3)', 1000)
// Preferred:
setTimeout(myFunc, 1000)
setTimeout(() => {
myFunc(1, 2, 3)
}, 1000)